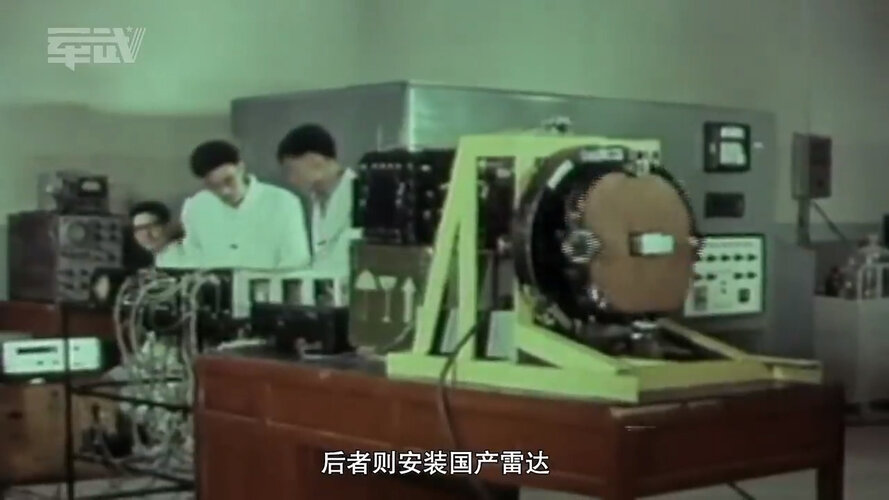
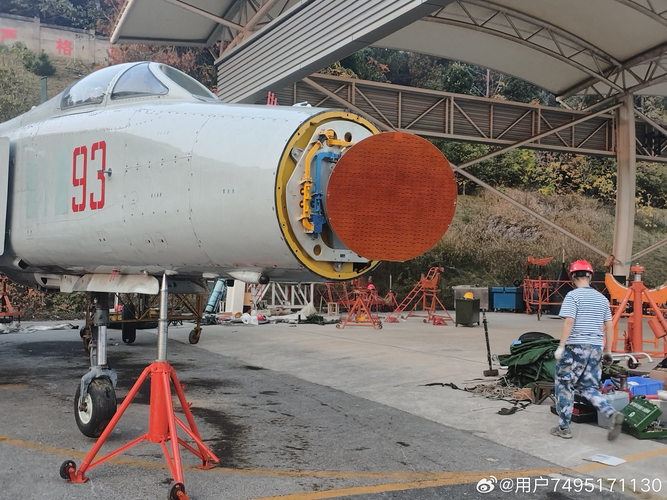
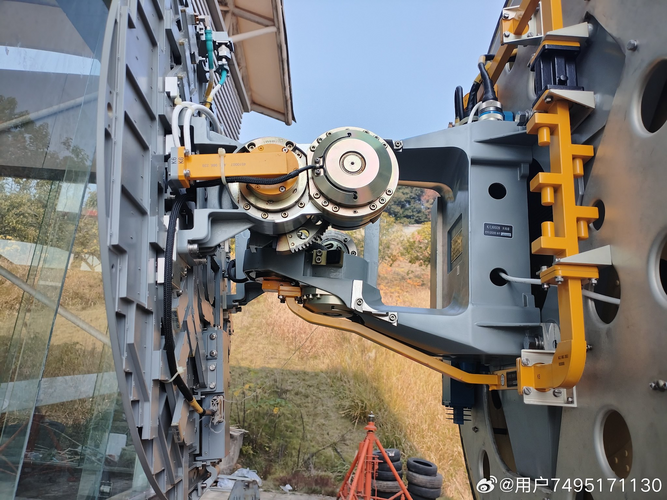
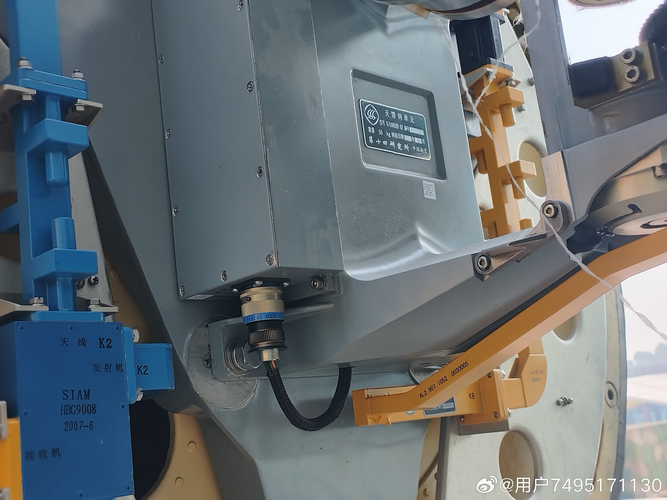
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Chinese Airborne Radars
- Thread starter overscan (PaulMM)
- Start date
- Joined
- 11 February 2010
- Messages
- 1,643
- Reaction score
- 2,682
Also, i visited Paralay's forum and found this. Apparently this is the AESA antenna intended for J-16.

----------
Going with Deino's post in previous page, for 1760 TRM count, Using Irbis-E size (90 cm, 0.63 sqm area) Showed element area of about 0.000357 sqm. Based on the arrangement of the array, it appears to use triangular lattice. Using the relationship of the element spacing (Anyone interested can read the deriviation in Chapter 13 of "Radar Handbook 3rd Edition" and assumption of full 120 degrees scanning. The frequency of the radar could be estimated to be 9136 MHz. If the antenna is Bars sized with 0.78 sqm. The frequency would be 8211 MHz.

----------
Going with Deino's post in previous page, for 1760 TRM count, Using Irbis-E size (90 cm, 0.63 sqm area) Showed element area of about 0.000357 sqm. Based on the arrangement of the array, it appears to use triangular lattice. Using the relationship of the element spacing (Anyone interested can read the deriviation in Chapter 13 of "Radar Handbook 3rd Edition" and assumption of full 120 degrees scanning. The frequency of the radar could be estimated to be 9136 MHz. If the antenna is Bars sized with 0.78 sqm. The frequency would be 8211 MHz.
Last edited by a moderator:
PDMODE
ACCESS: Restricted
- Joined
- 9 March 2023
- Messages
- 30
- Reaction score
- 110
Of course , I will try to find it when I over the busy work this week.Thank you! That series has a book a the J-10 and it’s creator. If you see it would you let me know? It might have useful stuff.
PDMODE
ACCESS: Restricted
- Joined
- 9 March 2023
- Messages
- 30
- Reaction score
- 110
Good news, I found it and I will upload it tomorrow.Thank you! That series has a book a the J-10 and it’s creator. If you see it would you let me know? It might have useful stuff.
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,712
- Reaction score
- 26,183
Removed some posts. Please don't upload or link to entire copies of published books in the forum.
China is getting better at IR imaging too

Breaking new ground in aerial imaging: the AVIID dataset and visible-to-infrared image translation
The rapid development of infrared technology, especially infrared cameras on UAVs, has expanded the applications of aerial infrared photography in military, industrial, agricultural, and environmental contexts.
www.eurekalert.org
Last edited by a moderator:
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
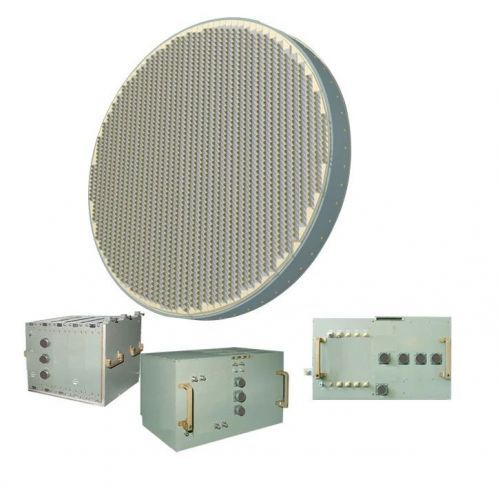
More on the J-16 radar
Attachments
- Joined
- 2 January 2006
- Messages
- 3,816
- Reaction score
- 5,014
More on the J-16 radar
Thanks ... most interesting is, we do not even have a designation for this radar!
PDMODE
ACCESS: Restricted
- Joined
- 9 March 2023
- Messages
- 30
- Reaction score
- 110
Type1493dThanks ... most interesting is, we do not even have a designation for this radar!
- Joined
- 2 January 2006
- Messages
- 3,816
- Reaction score
- 5,014
Type1493d
Oh! Thanks! ... but do you also know the designations of the PESA in the J-10B, the AESA used by the J-11BG and J-10C and most of all, I heard reports, the latest batch J-10S (or AS) refitted with WS-10B engines would already use an AESA too! Do you know here more too?
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
Attachments
Life of Tyo
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 23 January 2022
- Messages
- 71
- Reaction score
- 228
in description the history of J-8I this radar the interceptor , everyone know type of radar
View: https://youtu.be/sz6L6EiLI9k?si=pMPeK42q7BDpjWgx
Attachments
dinobeaning
ACCESS: Restricted
- Joined
- 27 November 2024
- Messages
- 2
- Reaction score
- 1
hello, sorry for the late ping, but do you have a source for this? i would love to read more.More on the J-16 radar
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
I don’t know what the original paper was titled unfortunately. I’ve only seen it cut uphello, sorry for the late ping, but do you have a source for this? i would love to read more.
Waterballoon
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 27 October 2023
- Messages
- 114
- Reaction score
- 226
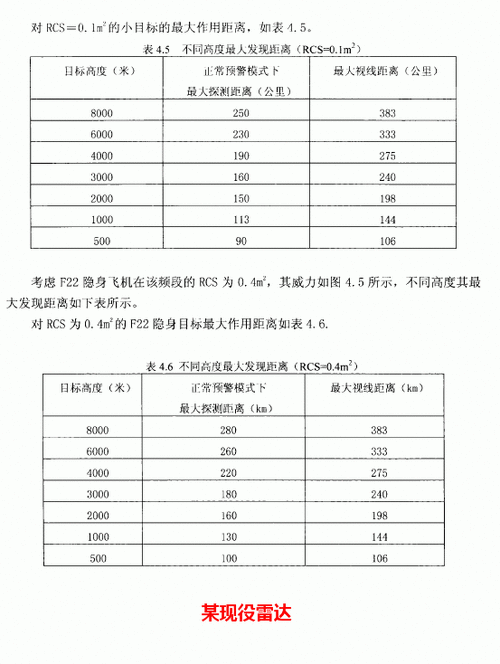
A 250km detection range against a 0.1 m2 target? That means 400km against a 1m2 target roughly.More on the J-16 radar
Hard to believe.
- Joined
- 11 February 2010
- Messages
- 1,643
- Reaction score
- 2,682
Yeah... i suspect it's from different paper on ground based radars as it mention Height. Not a problem for airborne radar but ground based one.
Eagle2009
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 8 February 2010
- Messages
- 172
- Reaction score
- 238
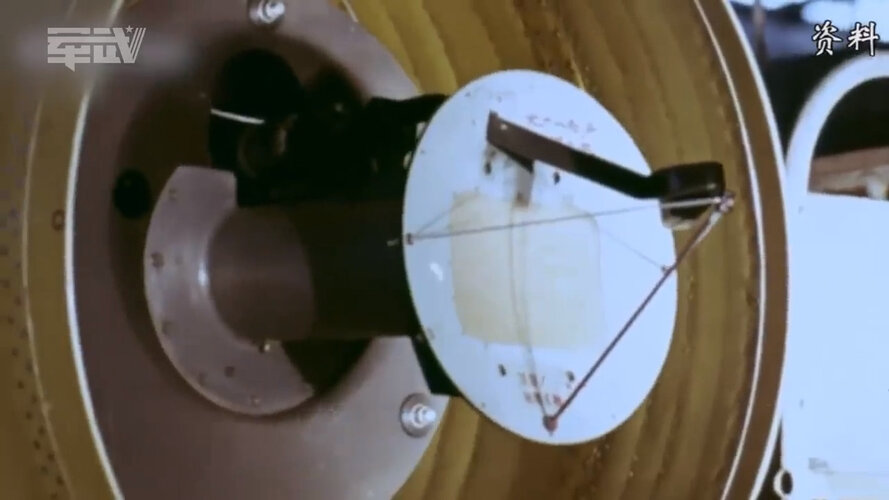
Not sure about the first image but the second image has an identical antenna design to existing images of the Type 204A radar, used in early J-8/I variants.in description the history of J-8I this radar the interceptor , everyone know type of radar
View: https://youtu.be/sz6L6EiLI9k?si=pMPeK42q7BDpjWgx
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
A 250km detection range against a 0.1 m2 target? That means 400km against a 1m2 target roughly.
Hard to believe.
I found a copy of the full paperYeah... i suspect it's from different paper on ground based radars as it mention Height. Not a problem for airborne radar but ground based one.
Attachments
- Joined
- 11 February 2010
- Messages
- 1,643
- Reaction score
- 2,682
Nice work. Guess those are for general AESA designs. not really specific on any fighters.
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
Yea I do no think they are for a particular fighter but I have seen the smaller one associated with the J-10B radar. I wonder if it’s the same technology, like a demonstrator.Nice work. Guess those are for general AESA designs. not really specific on any fighters.
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
电科14所:从1471到1493雷达的发展史_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
-, 视频播放量 13500、弹幕量 13、点赞数 331、投硬币枚数 28、收藏人数 227、转发人数 26, 视频作者 johnleo001, 作者简介 军工领域的考古爱好者。边挖掘边学习。。。,相关视频:14所雷达发展史:1492雷达的飞跃,凭实力“上户口”的JL-10A雷达,枭龙战机雷达完胜苏-30,歼10A即将换装JKL24有源相控阵雷达,性能强悍,歼10AG即将问事。,终极魔改版:歼-7MF,老式防空雷达屏幕里工作时啥样?来一起看看!,歼-10 防螺旋迎侧滑率大 飞控失效 发动机停车 警告,枭龙战机初代鹰眼:KLJ-7雷达,从五五项目到霹雳二号导弹,607所神鹰雷达的研制
Some footage I haven’t seen. Seems like a 14 institute radar history from J-8 but I can’t read Chinese.
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
Moreover, on Page 91, 全球防衛雜誌 Defence International 2007 April 272 reads:
“就雷達模式而言,Type 1473/KLJ-3目前應已具備完整的空對空能力,如單目標追蹤(STT)、掃瞄帶測距(RWS)、空中 近戰次模式/ACM Mode(HUD. Vertical scan, boresight, wide-angle acquisition. Stewing)、掃瞄帶追蹤(TWS)、速度搜索(Velocity search)、機群解析(raid assessment).空對地测距(AGR):至於空對面雷達模式包括都卜勒敏銳波(DBS)、真實波地面測繪(RBGM)、地面活動目標顯示(GMTI)、地面活動目標追蹤(GMTT),地形(TA)、固定目標追蹤(FTT)、地形追蹤(TF)、海面目標搜尋(SS).則可能僅完成部 份模式的驗證,多半的功能應在
發展或驗證中”
Which roughly translates to:
"As far as radar mode is concerned, Type 1473/KLJ-3 should currently have complete air-to-air capabilities, such as single target tracking (STT), scanning band ranging (RWS), air close combat sub-mode/ACM Mode (HUD, Vertical scan, boresight, wide-angle acquisition, Slewing), scanning band tracking (TWS), velocity search (Velocity search), fleet analysis (raid assessment), air-to-ground ranging (AGR): As for the air-to-ground radar mode Including Doppler sensitivity wave (DBS), real wave ground mapping (RBGM), ground moving target display (GMTI), ground moving target tracking (GMTT). terrain avoidance (TA), fixed target tracking (FTT). terrain tracking (TF) and Sea Target Search (SS), it is possible that only part of the model verification has been completed. Most of the functions should be under development or verification."
J-10A radar (1473), I would like to track down a copy of the primary source “ 全球防衛雜誌 Defence International 2007 April 272”
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
It is 1492, the model of the antenna ends with 92B.
Presumably 1491/1493
1493 was only used on the J-11B, this specific model of J-8 is the J-8DF which is using 1492.
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
I mixed 1491 And 1493 my apologiesIt is 1492, the model of the antenna ends with 92B.
1493 was only used on the J-11B, this specific model of J-8 is the J-8DF which is using 1492.
I mean 1491/1492
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
The author of that post was nice enough to give me the articleJ-10A radar (1473), I would like to track down a copy of the primary source “ 全球防衛雜誌 Defence International 2007 April 272”
Here is the page in question

再探新战鹰-J-10A亢龙战机
www.doc88.com

Thanks to the leap forward in information technology in the 1990s, it is speculated that the Type 1473/KLJ-3 currently installed on the J-10A has the latest technology level of traditional Doppler pulse radar, and its average power, maximum detection range, target tracking capability, pulse width, beam width, signal processing, sidelobes blanking & cancellation, anti-interference and waveform PRF interleafing capabilities are better than those of the Type 4.
Radars based on technology from the 1970s and 1980s are commonly used on modern fighter jets.
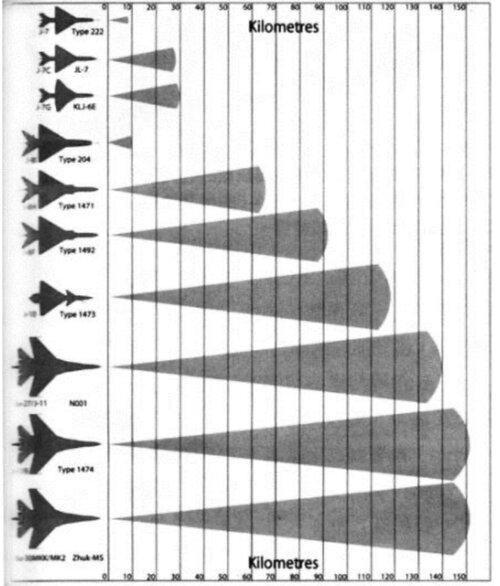
In terms of radar modes, the Type 1473/KLJ-3 should now have complete air-to-air capabilities, such as single target tracking (STT), scanning band ranging (RWS), air close combat sub-mode/ACM Mode (HUD, Vertical scan, boresight, wide-angle acquisition, Slewing), scanning band tracking (TWS), velocity search, raid assessment, air-to-ground ranging (AGR); As for air-to-surface radar modes, they include Doppler sensitive wave (DBS), true wave ground mapping (RBGM), ground moving target indication (GMTI), ground moving target tracking (GMT), and ground moving target tracking (GMT). (GMTT), terrain avoidance (TA), fixed target tracking (FTT), terrain tracking (TF), surface target search (SS), it is possible that only part of the mode verification has been completed, and most of the functions should be under development or verification, first meeting the needs of the main mission of air superiority operations, and then gradually expanding the air-to-surface mode, and finally achieving the full function of the radar (most Western radars also adopt this method)
Some reports indicate that the Type 1473/KLJ-3 has a maximum range of about 120~150km, can track 24 targets simultaneously and engage 6 targets simultaneously. Referring to the performance of the new Russian-made X-Band (8~12GHz) conventional Doppler pulse radar, such as the Kopyo-M Zhuk-MSE series, the average power is about 1.5KW, the maximum detection distance for an air target with an RCS of 5m2 is 85 and 180km respectively (40 and 80km for tail pursuit), and the target tracking and engagement capabilities are 10 (tracking)/4 (engagement) and 20/4 respectively. It can be judged that the radar of the J-10A should be better than the Kopyo-M and slightly inferior to the Zhuk-MSE-
Relevant section
F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
If you have an opportunity let me know. I’m doing so reading on Chinese radars and this would be helpful.If you are getting this from the two reports linked above, I don't agree this describes KLJ-1. Will post my argument later.
Also I made an attempt to make a PDF of the report based on screenshots
Attachments
Similar threads
-
China's J-10 Radar : NRIET Type 1473 and questions
- Started by overscan (PaulMM)
- Replies: 7
-
GEC Marconi Skyranger / Super Skyranger
- Started by JFC Fuller
- Replies: 6
-
1944 H2D Pulsed Doppler Radar - True or Misidentified?
- Started by GUNDAM123dx
- Replies: 1
-
-
NPO Istok "Soyuz-Sintez" Experimental Radar program
- Started by overscan (PaulMM)
- Replies: 18