If someone has time to redo the list incorporating
@PhR revisions, I think we should lock this topic and start a new one with a revised list as a starting point. I might get time to do it myself.
I tried to do the exercice, I I have to agree that this is a very difficult work. I was not able to verify all entries. First part:
Regular 2 and 3-digit designations:
SE.10 was a generic designation for
SE.100 C3 projects family
SE.11 was a generic designation for
SE.101 and
SE.110 C3 projects family
SE.12 was a generic designation for
SE.102 and
SE.103 AB3 projects family
SE.010 was a pre-study for reconnaissance seaplane that became
SE.400
SE.011 was a pre-study for a seaplane that became
SE.900, 1941-42
SE.012 was a pre-study for version with redesigned wings and stratospheric cabin of the
LeO.457, powered by 2 Hispano-Suiza 12Z with compressors
SE.014 initially called
SE.200C Amphitrite C was a pre-study for a 110 ton long-haul seaplane that became
SE.1100, 1941-43
SE.015 was a pre-study for a four-engine stratospheric transport aircraft that became
SE.1000, 1941
SE.016 was a pre-study for a light passenger plane, 1942
SE.017 was a pre-study for a training seaplane, 1942
SE.018 was a pre-study for a transport autogiro, powered by one Gnome-Rhône 14M engine, 1941
SE.050 was a pre-study for a 50 ton transatlantic four-engine aircraft that became
SE.2000
SET.053 was a pre-study for a light flying wing passenger plane that became
SE.2100
SE.100 was a twin-engine three-seater fighter (C3) initially designed as
LeO.50, powered by two 950 hp Gnome-Rhône 14N-20/21, then 14N48/49 engines. 1936, 2 prototypes ordered, only 1 finished, 1st flight 29th March 1939
SE.101 was the former
SE.110, a three-seat fighter in C3 category, powered by two 580 hp Hispano-Suiza 14AB engines or Gnome-Rhône 14N20/21 or 14N48/49. 1937, 1 ordered, not finished
SE.102 was a three seat observation light bomber version, in AB3 category, powered by two Gnome-Rhône 14 N2/3 or 14N40/41 or 14N44/45 engines. 1939, 2 ordered, not finished
SE.103 was an AB3 version of the
SE.102, powered by two 1150 hp Hispano-Suiza 14AA-12/13 engines. 1938, 1 prototype ordered, became SE.100-03, never finsihed
SE 104 was a long-range transatlantic flying boat project (9 tons of cargo + 70 passengers)
SE.105 was the former second
SE.102, with two auxiliary tanks and powered by two 1320 hp Gnome-Rhône 14 R4/5 engines. 1939, not finished
SE.110 was an initial designation for
SE.101
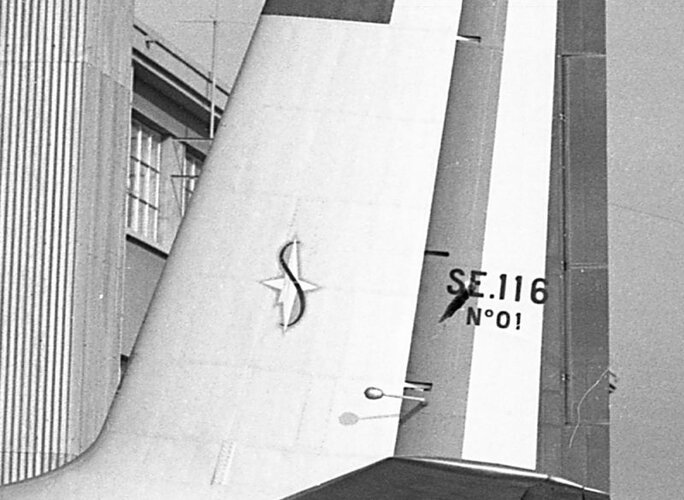
SE.116 Voltigeur was a two-seater twin-engine fire support aircraft, initially designed as
X.116, powered by two 800 hp Wright C7-B1 engines (
SE.116A c/n 01) or two 760 hp Turboméca Bastan turboprops (
SE.116B c/n 02). 2 prototypes, 1st flight 5th June 1958
SE.117 Voltigeur was a third prototype of
SE.116 with enlarged fuselage, powered by two 760 hp Turboméca Bastan turboprops. Two version studied:
SE.117A with radial piston engines and
SE.117B with turboprops. 1 prototype, 1st flight 21st January 1960
SE.118 Diplomate was an 8-10 seater transport plane derived from
SE.116/117, powered by two 760 hp Turboméca Bastan turboprops. 1958, 1 prototyped, not finished
SE.119 was a project derived from
SE.117. Not built
SE.122 was a single seat experimental plane inspired from
SE.100, a scale down configuration, powered by single engine, driven two counter-rotating propellers. Project only
SE.161 Languedoc was a thirty-three-seat transport monoplane, started as Bloch
MB.161, then became
SO.161 Bordeaux. 1936, 1 prototype + 101 built + 4 not finished, 1st flight 15th December 1939
SE.200 Amphitrite was a formerly
LeO.H49, 70 ton large transport transatlantic flying boat, powered by six 1600 hp Gnome-Rhône 14R-26/27 engines. 4 ordered, 2 not finished, 1st flight 8th October 1942
SE.200C Amphitrite C was a pre-study for a 110/120 ton long-haul seaplane that became
SE.014, then
SE.1100, 1941-43. Project only
SE.203 was a version of the
SE.200, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 14R engines, and 68 ton empty weight. Project only
SE.204 was planned to be the
SE.200 c/n 4 with enhanced performances, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 18R engines, and 80 ton empty weight. Project only
SE.204M was a military version of
SE.204, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 18R engines, with defensive and offensive weapons
SE.201 Aquilon was a two-seat night pursuit version of 1952
SE.202 Aquilon was a DH Sea Venom derivative
SE.203 Aquilon was a single seat fighter version
SE.204 Aquilon was a two-seat jet trainer version
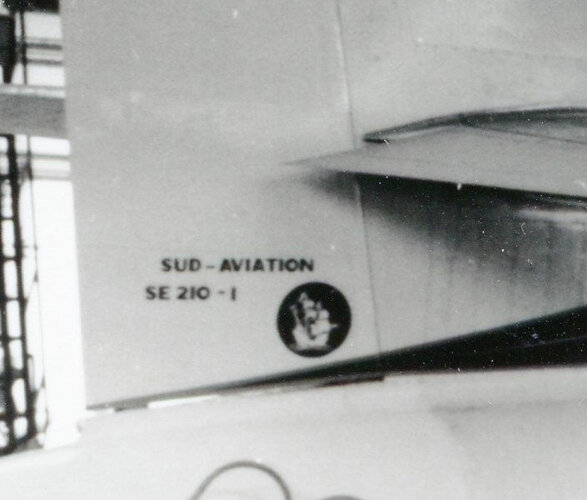
SE.210 Caravelle was a twin-engine jet transport aircraft, initially designed as
X.210. 2 prototypes + 280 copies, 1st flight 27th May 1957
SE.210 Nuclear was a version of Caravelle, fitted with two nuclear-powered engines. Project only
SE.212 was a Project version of
SE.200, powered by six Gnome-Rhône 18R, wing area increase of 35 m and 90 ton empty weight
SE.212 Durandal was a single-seat single-engine light interceptor, derived from
X.212 initial design. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 20 April 1956
SE.212 Durandal I/1 was an early design with large delta wing, fitted with mixed powered engine. Project only
SE.212 Durandal I/2 was a second design with small delta wing, fitted with mixed powered engine. Project only
SE.212 Durandal III was Project version, had a side-intakes and high delta wing, also fitted with skids to land, fitted with mixed powered engines. Project only
SE.212 Durandal IV was a Project as interceptor version, with small radome for radar, powered by one Snecma ATAR 9 plus rocket engine. Project only
SE.212 Durandal IVM was an aircraft carrier based version, powered by one Snecma ATAR 9 engine. Project only
SE.216 Fonceur was experimental COIN aircraft. Project only
SE.247 was developed from
LeO.H47, as a military derivative version of 1945. Project only
SE.300 was a three-seater twin-engine “work” plane (category T3), initially designed as Romano
R.111. 1937, project only
SE-300 was supposed to be a light transport autogiro project, powered by one 350 hp Gnome-Rhône engine (not confirmed)
SE.300T seaplane wind-tunnel model was a tested in Toulouse. Project only
SE.301 wind-tunnel model was tested as in Toulouse. 1941, project only
SE.400 was a three-seat mid-wing surveillance plane, on floats (c/n 01) or on weels (c/n 02), powered by two 655 hp Gnome-Rhône 14M engines (c/n 01) or two Lorraine Algol (c/n 02). 2 prototypes, 1 not finished, 1st flight 31st December 1939
SE.500 was a four seat light bomber project derived from
SE.100, powered by two 1050 hp Gnome-Rhône N-48/49 or 1600 hp Gnome-Rhône 14R engines. Project only
SE.500T was a twin-engine 12 passenger cargo/transport Project, powered by two 1050 hp Gnome-Rhône 14R engines. Project only
SE.520Z was the former Dewoitine
D.520 N°372 fitted with one Hispano-Suiza 12Z engine. 1 built, 1st flight 22nd October 1948
SE.530 Mistral was a license built De Havilland Vampire
SE.531 Mistral was a license built De Havilland Vampire with Nene 102B engine
SE.532 Mistral was a license built De Havilland Vampire with Nene 104 engine and ejector seat
SE.535 Mistral was a naval fighter version of De Havilland Vampire Mk 50 modified and built by SNCASE. 247 copies
SE.580 was a post-war project fighter derived from
D.520 with dorsal air intake, powered by one Hispano-Suiza 12Z engine. Initially designed as
M.580, then became
SET.580. 2 ordered, not finished
SE.581 was a Project version of
SE.580, powered by one 2500 hp Hispano-Suiza 24Z engine, became
SET.581. 1 not finished
SE.582 was a project version of
SE.580, powered by one 4000 hp Arsenal 24H engine. Project only
SE.600 was a generic study for a two-seat experimental aircraft family derived from
SE.100, powered by one 350 hp Bearn 6D engine. Projects only
SE.700 Alouette was a three-seat passenger autogiro, powered by one 330 hp Béarn 6D-07 engine. 4 ordered, 1 built, 1st flight 25th May 1945
SE.701 Alouette A was a version of the
SE.700, intended to carry 700 kg of load, powered by one 220 hp Renault 6Q-01 engine, also known as
SE.700A. Project only
SE.702 Alouette B was a version of the
SE.700, featured by a fuselage hull and a fixed front wheel, powered by one 330 hp Béarn 6D-07 engine, also called
SE.700B. Project only
SE.800 was a transport project developed from
SE.100, 22 passenger and four crew, powered by either two or four 1350 hp Gnome-Rhône 14 or 1650 hp Wright Cyclone engines. Project only
SE.800A was a 24 passenger and four crew variant of
SE.800, powered by two 1300 hp Gnome-Rhône 14 R engines. Project only
SE.800B was a 33 passenger and four crew variant of
SE.800, powered by four 1000 hp Hispano-Suiza 12 Y engines. Project only
SE.800C was a 24 passenger in pressurized cabin variant of
SE.800, powered by two 1600 hp Gnome-Rhône 14 R engines. Project only
SE.900 was a seaplane initially designed as
SE.011. 1941-42, project only
Marignane design office (Mercier, Poitou, Gross, Hertel) SE.1xxx slot:
SE.1000 was a mid-wing stratospheric transport monoplane, initially designed as
SE.015, powered by four 1590 hp Gnome-Rhône 14 R engines. 1942, 1 prototype not finished
SE.1001 was a Project version of
SE.1000, with re-designed the nose and cockpit configuration, as a long-range mail carrier. Project only
SE.1010 was a high-altitude photo-survey aircraft derived from
SE.1000, powered by four 1600 hp Gnome-Rhône 14 R-28/29 engines. 1 prototype built, 1st flight 23rd November 1948
SE.1011 was a production aircraft powered by four Bristol Hercules engines. 3 pre-series under construction, not finished
SE.1015 was a long-range 18 passenger courier airliner, powered by four 1600 hp Gnome-Rhône 14R-28/29 engines. Project only
SE.1020 was a maritime patrol aircraft Project, with gun turret, powered by four Junkers Jumo 213 engines. 1946, project only
SE.1030 was a proposed 45 passenger airliner variant, powered by four 1600 hp Gnome-Rhône 14R-28/29 engines. 1947, project only
SE.1035 was a high speed stratospheric airliners for 44-48 passengers with a more conventional larger diameter airliner. 1947, project only
SE.1040 was a proposed turboprop test-bed to evaluate the Rolls-Royce Dart engine. 1949, project only
SE.1100 was a redesign of
SE.200C Amphitrite C, then
SE. 014, as a heavy civil/military transport flying boat Project, 120 ton empty weight. 1942, project only
SE.1200 was a medium transport compound helicopter for 8 passengers, with shoulder wing and addition two piston engines, mounted on it and the a low rear wing with twin tail fins. 1943, project only
SE.1200 was a 140 ton 125 passenger heavy seaplane derived from
SE.1100, powered by eight 3400 hp Arsenal 24H engines, 140 ton empty weight. 1946, project only
SE.1210 was a 1/2.9 sub-scale flying model of
SE.1200, powered by four 220 hp Renault 6Q-20/21 engines. 1 built, 1st flight 9th June 1948
SE.1300 was a fast transport seaplane derived from the
SE.1200, with 180 ton empty weight. 1945-46 project only
SE.1400 was a side-by-side two seat attack aircraft derived from
SE.2400, powered by two Hispano-Suiza Nene turbojets, mounted beside the fuselage with wing roots, later redesigned and developed into
SE.2450. Project only
SE.1400 was a projected single-seat sub-scale flying mock-up of
SE.2400, powered by one Rolls Royce Derwent V turbojet engine. 1948, project only
SE.1410 was a projected sub-scale flying mockup of
SE.2400, powered by Walter HWK 109/509 rocket engine. Project only
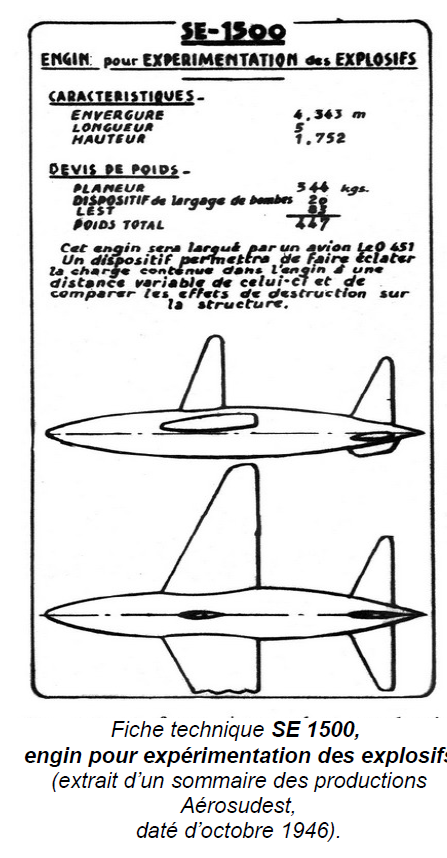
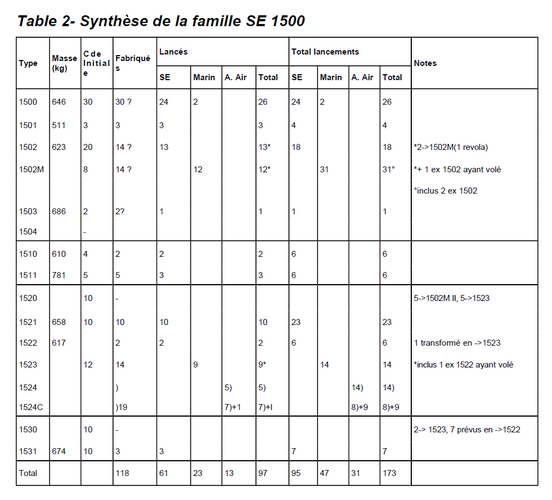
SE.1500 was a remote-controlled gliding target. 1946, ~100 built, including all variants
SE.1501 was a unguided target (1948)
SE.1502 was a unguided target (1950)
SE.1502M was a Navy recoverable target (1953)
SE.1503 was a turbojet powered target (1953)
SE.1510 was a guided and recoverable target (1948)
SE.1511 was a test of optical guidance (1952)
SE.1520 was built but not flown; five were modified into SE 1502M and five more into SE 1523
SE.1521 was an experimental flying bomb (1949)
SE.1522 was a recoverable target (1952)
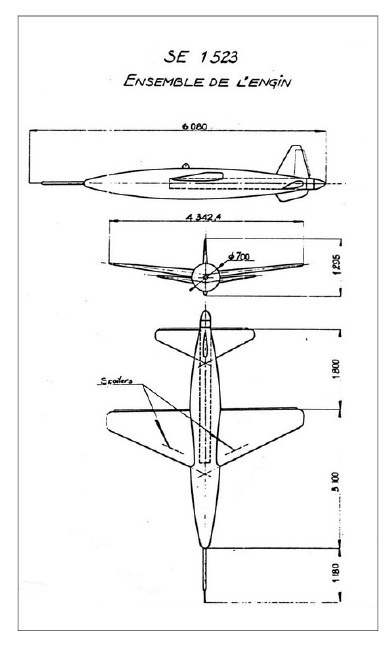
SE.1523 was a Navy operational recoverable target (1953)
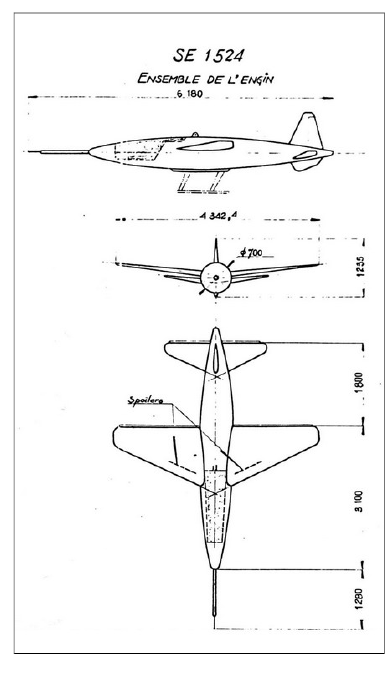
SE.1524 was an Air Force operational recoverable target (1953)
SE.1530 was a built and not flown; seven were modified into SE 1522 and two into SE 1523.
SE.1531 was a rocket powered variant (1952)
SE.1600 was a ground-to-ground missile with additional vertical control surfaces, designed to be launched by
SE.1900. Project only
SE.1610 was a version of
SE.1600 powered by pulse-jet. Project only
SE.1700 was a flying-wing ground-to-ground missile, designed to be launched by
SE.1900. Project only
SE.1800 was a two-seat experimental twin-engine flying wing civil transport jet or bomber, powered by two Rolls Royce Nene turbojet engines. 1946, project only
SE.1801 was a version of
SE.1800 twin-engine flying wing, powered by two Rolls Royce Nene engines. 1946, project only
SE.1802 was a version of
SE.1800 twin-engine flying wing, powered by two Snecma ATAR 101 turbojet turbojet engines. 1946, project only
SE.1900 was a rocket-powered wheeled cart. 1 built
SE.1910 was a version on rails of
SE.1900 rocket-powered cart, speed record breaker. 1 built
Toulouse design office (Satre) SE.2xxx slot:
SE.2000 was a 50 ton mid-wing transatlantic heavy transport, initially designed as
SE.050, powered by four 2100 hp Gnome Rhône R18 engines. 1945, project only
SE.2000 was a B6/R6 heavy bomber, powered by four 2100 hp Gnome Rhône R18 engines. 1944, project only
SE.2010 Armagnac was an enlarged version of
SE.2000 transatlantic, with a cantilever mid-wing monoplane with retractable tricycle landing gear, powered by four 3500 hp Pratt & Whitney R-4360-B13 Wasp Major engines. 1 prototype + 8 built, 1st flight 2nd April 1949
SE.2020 was a version of
SE.2010 with bigger wheels (1, 72 m instead of 1, 52 m). Project only
SE.2030 was a version of
SE.2010, but powered by four Cyclone turboprop engines. Project only
SE.2040 was a derivative of
SE.2010, with four Allison T40 turboprop engines and longer fuselage. Project only
SE.2043 was a version of
SE.2040, powered by four Bristol Proteus turboprop engines. Project only
SE.2060 was the
SE.2010 c/n 3 transformed as jet engine test bed aircraft for Snecma , fitted with two Atar 9D, 9K, TF.104, TF.106, or TF.306 jet engines. 1 modified
SE.2100 was a two-seat light and touring tailless airplane, initially designed as
SET.053, powered by one 140 hp Renault 4Pei pusher engine. 1 built, 1st flight 4th October 1945
SE.2200 was a temporary designation of the
SE.580 single seat naval fighter. April 1943
SE.2300 was a two-three seat low-wing light and touring monoplane with conventional landing gear, powered by one 140 hp Renault 4Pei engine. 1 built, 1st flight 26th October 1945
SE.2310 was a three-seat, tricycle undercarriage version, powered by one 140 hp Renault 4Pei engine. 2 built, 1st flight 31st December 1945
SE.2311 was a version of
SE.2310, powered by one 135 hp Régnier 4L-00 engine. 1 built, 1st flight 27th October 1947
SE.2320 was a version of
SE.2310 with retractable gear, powered by one 135 hp Régnier 4L-00 engine. Project only
SE.2400 was a low-mid-wing single seat experimental attack monoplane Project, powered by two Socema CEM turbojet engines, mounted under each wing. 1946, project only
SE.2400 was a single seat mid-wing experimental attack monoplane, powered by two Rolls Royce Nene turbojet engines mounted in dorsal intakes. 1946, project only
SE.2410 Grognard I was a single seat low-level ground attack experimental monoplane prototype, powered by two Hispano-Suiza Nene 101 turbojet engines. 1 prototype, 1st flight 30th April 1950
SE.2411 Grognard was a developed version from
SE.2410, powered by two Rolls Royce Nene 102 turbojet engines. 2 ordered, never built, abandoned in favor of
SE.2415
SE.2415 Grognard II was a two-seat as a development version, that included a stretched fuselage incorporating a raised cockpit with a bubble canopy and increased 39˚ wing sweep back, powered by two Rolls Royce Nene 102 turbojet engines. 1 single-seat prototype, 1st flight 14th February 1951
SE.2416 Grognard was a single seat strike aircraft version of
SE.2400, with four HS 603 30mm machine guns, also the same engines. Project only
SE.2417 Grognard was a
SE.2415, re-engine with Tay or Verdon turbojets, and fitted with eight 20mm guns. Project only
SE.2418 Grognard was a single seat attack “final” version of
SE.2415, this design mated a 47° highly swept wing fuselage, with two 30mm guns, powered by two Rolls-Royce Tay or two Snecma ATAR 101F turbojet engine. Project only
SE.2419 Grognard was a direct adaption of
SE.2418 with wings from
SE.2410, powered by two Rolls Royce Nene turbojets, and two 30mm guns. Project only
SE.2420 Grognard III was a single or twin-seat all-weather fighter, based on third
SE.2415 prototype with thin wings, powered by two Tay turbojets. 1948-50, 1 under manufacturing, never completed
SE.2421 Grognard was a two-seat long-range all-weather fighter Project, based on
SE.2420 fitted with radar and wings from
SE.2410, powered by two Tay turbojets. Project only
SE.2422 Grognard was a single seat strike aircraft derived from
SE.2420, with thin wings and featured a revised air-intakes (lesser bulky but wider), powered by two Tay turbojets. Project only
SE.2422R Grognard was a single seat recce version of SE.2422, with cameras in place of gun bay
SE.2423 Grognard was a design version, mated the fuselage of
SE.2418 with the wings of
SE.2415. Project only
SE.2424 Grognard was another version of
SE.2418, but with Snecma Vulcain P-150 engines with post combustion. Project only
SE.2450 Grognard was a simplified
SE.2400, side-by-side two-seat with bubble canopy and pursuit radar, and powered by two Hispano-Suiza Nene turbojets, mounted beside the fuselage with wing roots. Initially designated
SE.1400 at Marignane, became
SE.2450 when transferred to Toulouse. Project only
SE.2500 was a designation mentioned as similar to the X.201.02.01, jet airliner. Project only (Not confirmed)
SE.2600 was a ground-to-air rocket engine for SA.20 program. Project only
SE.2610 was a reduced model of
SE.2600. Project only
Courbevoie, then Marignane design office (Renoux, Focke, Marchetti, Mouille) SE.3xxx slot:
SE.3000 was a heavy two rotor transport helicopter, built using captured Focke-Achgelis Fa 223 parts, powered by one 1000 hp Bramo Fafnir BMW 323 R2. 1 prototype + 2 built, 1st flight 23rd October 1948
SE.3100 was a twin-engine single-rotor large transport helicopter for 8 to 12 passengers, with unusual “butterfly” angled twin tail rotors, powered by two Gnome-Rhône 14R54 engines. Project only
SE.3101 was an experimental sub-scale prototype version of
SE 3100, powered by one 100 hp Mathis 4G20 engine. 1 prototype, 1st flight 16th June 1948
SE.3110 was a two-seat experimental light helicopter, powered by one 200 hp Salmson 9Nh engine, with “butterfly” tail rotors. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 16th June 1950
SE.3111 was a variant of
SE.3110 fitted with rotors larger diameter tail (2.80 m instead 2.40 m). Project only
SE.3120 Alouette was a single seat crew and two seat utility helicopter, powered by one 203 hp Salmson 9Nh engine. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 31st July 1951
SE.3130 Alouette II was an enlarged version of
SE.3120, with one crew and four seat, utility and multi-role helicopter, based on
X.310G pre-study design for powering a light helicopter with turbine engine, powered by one 530 hp Turbomeca Artouste IIC6 turboshaft engine. Became
SA.313 in 1968. 3 prototypes + 2 pre-series + 923 built, 1st flight 12th March 1955
SE.3131 Gouverneur was the
SE.3130 c/n 1055 temporarily modified with faired fuselage. 1 modified, 1st flight 10th May 1957
SA.313 Alouette II was the new designation of
SE.3130 adopted in 1968
SE.3140 Allouette-Turmo was a
SE.3130 temporarily modified with shorter main rotor blades and one 400 hp Turbomeca Turmo turboshaft engine. Became
SE.3150 after re-engined. 1 modified, 1st flight 16th May 1957
SE.3150 was enhanced
SE.3130 for high altitude operation, fitted with larger main rotor, 3-blade tail rotor and powered by one 500 hp Turbomeca Artouste III turboshaft engine. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 11th March 1958. Became
SA.315A and
SA.315B Lama
SA.315 Lama was the production version of the
SE.3150, also called "
Cheetah" in India and "
Giviaõ" in Brazil. 383 built?
SE.3160 Allouette III was a redesigned Alouette II with all-metal monocoque fuselage, and a fully enclosed seven-seat cabin and fixed tricycle undercarriage, powered by one 870 hp Turbomeca Artouste IIIB turboshaft engine. Became
SA.316 in 1968. 2 prototypes + 4 pre-series + 200 built, 1st flight 28th February 1959
SA.316 Alouette III was the new designation of
SE.3160 adopted in 1968
SE.3164 Alouette-canon was a
SE.3160 temporarily with stepped windshield and nose-mounted 20mm gun. 1 prototype, 1st flight 24 June 1964
SE.3180 Alouette II was a version of the
SE.3130 re-engined with 450 hp Turbomeca Artouste II turbine. Became
SA.318 in 1968. 3 prototypes + 382 built, 1st flight 31st January 1961
SA.318 Alouette II was the new designation of
SE.3180 adopted in 1968
SA.319 Alouette III was the
SE.3160 fitted with 600 hp Turbomeca Astazou XIV turboshaft engine. 1 prototype + 1 pre-series + 1455 built, 1st flight 27th June 1968
SE.3200 Frelon was a heavy transport helicopter with single four-blade main rotor, powered by three 750 hp Turbomeca Turmo IIIB turboshaft engines, positioned in housing on top of fuselage. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 10th June 1959
SA-3210 Super Frelon was a heavy three-turbine helicopter developed with support from Sikorsky after the failure of
SE.3200, with boat hull and outrigger floats, rear loading doors, boom tail
siX.blade main rotor driven three 1320 hp Turbomeca Turmo IIIC turboshaft engines. 2 prototypes + 4 pre-series, 1st flight 7th December 1962
SA.321 Super Frelon was the production version of the
SE.3210. 99 built
SA.3220 Frelon was a production version of the
SE.3200, total mass 10 ton, with single five-blade main rotor, the waterproof hull was extended at the front by a bow and bent tail (foldable) used to raise the anti-torque rotor, powered by three 1250 hp Turbomeca Turmo IIIC turboshaft engines. 1960, project only
SA.3230 was a twin-engine heavy helicopter derived from
SE.3200, powered by two 1320 hp Turbomeca Turmo IIIC turboshaft engines. 1960, project only
SA.330 Puma was a medium-lift 20 troop military helicopter with retractable tricycle undercarriage and single four-blade main rotor, powered by two 1320 hp Turbomeca Turmo IIIC4 turboshaft engines. 2 prototypes + 6 pre-series + >697 built, 1st flight 15th April 1965
SA.331 was a project derived from SA.330, Powered by two Turboméca Makila engines and “fenestron” tail-rotor. 2 technical demonstrators temporarily modified: former SA.330-02 fitted with Makila engines and SA.330-05Z with fenestron
SA.340 Gazelle was a light five-seat multi-role helicopter, with streamlined fuselage, tail rotor, three-blade main rotor, powered by one Turbomeca Astazou IIN2 turboshaft engine, based on
X.300 design. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 7th April 1967
SA.341 Gazelle was the production version of
SA.340. 4 pre-series + many built
SA.342 Gazelle was an enhanced version of
SA.341. Many built
SA.349Z and
SA.349-2 were the former SA.340-01 and SA.342K-1201 modified with wings as experimental helicopter. 2 prototypes
Marignane design office (Poitou) then Cannes (Gross) SE.4xxx slot:
SE.4000 was a high-wing amphibian flying boat light transport Project, powered by one 450 hp Mathis 16G pusher engine, mounted above the wing, initially designed as
X.104. 1948-49, project only
SE.4020 was a twin-engine amphibious seaplane, powered by two 330 hp De Havilland Gipsy Queen 70 engines. 1949, project only
SE.4030 was a high-wing amphibian flying boat light transport Project, enlarged version of
SE.4000, powered by two Armstrong Siddeley Cheetah or P&W engines, in tractor position. 1949-50, project only
SE.4040 was a light transport aircraft, land version of the
SE.4030, powered by two 410 hp Armstrong-Siddeley Cheetah 10 engines. 1949, project only
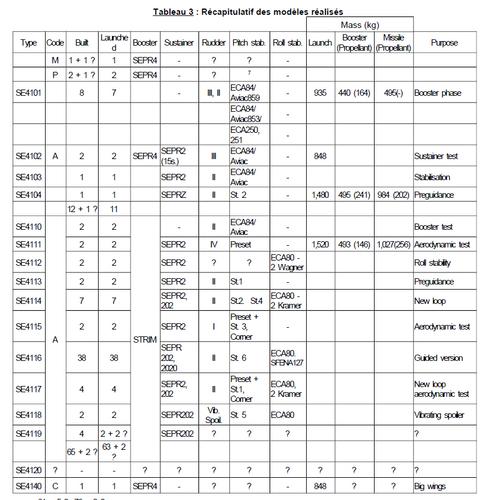
SE.4100 was a first French rocket, former
NC.3500. 3 built, 1st launch 29th September 1949
SE.4101 was the first derived version of
SE.4100. 8 launched
SE.4102 was a version of
SE.4100 with SEPR2 rocket and additional cruise boosters. 2 launched
SE.4103 was a version of
SE.4100 with automatic pilot. 1 launched
SE.4104 was a version of
SE.4100 with STRIM auxiliary booster. 1 launched
SE.4110 was a version of
SE.4100 with STRIM auxiliary booster. 1 launched
SE.4111 was a version of
SE.4100 with SEPR2 rocket and STRIM auxiliary booster. 2 launched
SE.4112 was a version of
SE.4100 with ECA 80 gyroscope. 2 launched
SE.4113 was a version of
SE.4100 with ECA control command. 2 launched
SE.4114 was a version of
SE.4100 with SFENA control and STRIM auxiliary booster. 7 launched
SE.4115 was a version of
SE.4100 with modified control surfaces. 2 launched
SE.4116 was the 1st guided version of
SE.4100. 38 launched
SE.4117 was a version of
SE.4100 with modified control surfaces. 4 launched
SE.4118 was a version of
SE.4100 with modified control law. 2 launched
SE.4119 was a guided version of
SE.4100. 2 launched
SE.4120 was a version of
SE.4100 with modified control surfaces. Project only
SE.4140 was a variant of
SE.4100 with modified wing surface. 1 launched
SE.4200 was a first operational ramjet-powered ground-to-ground missile. Former
NC.3510 designed for SS.40 program. 2 built, 1st launch 8th February 1950
SE.4201 was a variant of
SE.4200. 2 built, 1st launch 7th March 1950
SE.4202 was a variant of
SE.4200. 2 built, 1st launch 27th April 1950
SE.4203 was a variant of
SE.4200. 9 built, 1st launch 3rd October 1950
SE.4204 was a variant of
SE.4200. 4 built, 1st launch 3rd October 1950
SE.4205 was a variant of
SE.4200. 16 built, 1st launch 12th December 1950
SE.4206 was a variant of
SE.4200. 4 built, 1st launch 26th June 1951
SE.4207 was a variant of
SE.4200. 34 built, 1st launch 18th March 1952
SE.4208 was a variant of
SE.4200. 19 built, 1st launch 19th February 1953
SE.4209 was a variant of
SE.4200. 2 built, 1st launch 6th May 1953
SE.4210 was a variant of
SE.4200. 4 built, 1st launch 30th May 1954
SE.4211 was a variant of
SE.4200. 27 built, 1st launch 30th September 1954
SE.4212 was a variant of
SE.4200. 4 built, 1st launch 22nd June 1954
SE.4213 was a variant of
SE.4200. 2 built, 1st launch 20th August 1954
SE.4220 was a variant of
SE.4200. 2 built, 1st launch 14th February 1955
SE.4230 was a variant of
SE.4200. 2 built, 1st launch 14th December 1954
SE.4241 was a variant of
SE.4200. 26 built, 1st launch 8th March 1955
SE.4242 was a variant of
SE.4200. 82 built, 1st launch 3rd June 1955
SE.4243 was a variant of
SE.4200. 4 built, 1st launch 18th October 1955
SE.4243 was a variant of
SE.4200. Not built
SE.4245 was a variant of
SE.4200. 30 built, 1st launch 13th November 1956
SE.4246 was a variant of
SE.4200. 94 built, 1st launch 25th February 1958
SE.4247 was a variant of
SE.4200. 20 built, 1st launch 6th June 1957
SE.4261 was a variant of
SE.4200. 32 built, 1st launch 20th October 1954
SE.4262 was a variant of
SE.4200. 10 built, 1st launch 7th June 1958
SE.4263 was a variant of
SE.4200. 60 built, 1st launch 8th June 1955
SE.4270 was a variant of
SE.4200. Not built
SE.4280 was a variant of
SE.4200. 108 built, 1st launch 5th May 1959
SE.4290 was a variant of
SE.4200. Not built
SE.4300 was a surface-to-air vehicle with SEPR 053 dual-liquid rocket. 86 built, 84 launched, 1st launch 27th February 1954
SE.4350 was a variant of
SE.4300 with SEPR 50531 rocket. 89 built, 41 launched
SE.4400 was a ramjet-powered ground-to-air missile. 74 built, 1st launch 9th April 1954
SE.4401 was a variant of
SE.4400. 18 built, 1st launch 4th June 1954
SE.4402 was a record-breaking variant
SE.4400
SE.4500 was an enlarged ramjet-powered version of the
SE.4200 intended to carry a 700-kg bomb at a distance of 130 kms. 62 built, 1st launch 10th October 1956
Argenteuil design office (Jakimiuk) SE.5xxx slot:
SE.5000 Baroudeur was a single seat high-wing lightweight strike fighter monoplane, powered by one Snecma ATAR 101D turbojet engine. 2 prototypes, 1st flight 1st August 1953
SE.5002 Baroudeur A was a smaller version, powered by one Bristol Siddeley Orpheus II turbojet engine. Project only
SE.5003 Baroudeur was a pre-series version, powered by one 3700 kgs thrust ATAR E5 turbojet engine. 3 built, 1st flight September 1955
SE.5004 Baroudeur was a version, powered by one Snecma ATAR E4 engine. 1957, project only
SE.5008 Baroudeur was a proposed series version with a 4700 kgs thrust Snecma ATAR 8 engine. 1957, project only
SE.5008 VS Baroudeur was a variant of
SE.5008 with blown wing. Project only
SE.5010 Baroudeur L was a light tactical support variant, powered by one Bristol Siddeley Orpheus engine. 1953, project only
SE.5012 Baroudeur was a proposed series version of
SE.5000, powered by one Bristol Siddeley Orpheus 12 engine. 1957, project only
SE.5013 Baroudeur was based on
SE.5002, with Bristol Siddeley Orpheus engine, and a blown wing. Project only
SE.5020 Baroudeur S was proposed single-engine tactical support aircraft version of
SE.5000, with a lightened airframe, powered by one Snecma ATAR M engine. 1953-54, project only
SE.5030 Baroudeur R was a derived version of
SE.5000, powered by one Snecma M17 engine. 1954, project only
SE.5040 Baroudeur O was a reduced at 8/10 scale lightweight version of
SE.5000, powered by one Bristol Siddeley Orpheus. 1957, project only
SE.5050 Baroudeur was developed from
SE.5091, with blown wing and Snecma ATAR engine. Project only
SE.5091 Baroudeur was a Project in collaboration with Fiat