F-2
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 22 May 2020
- Messages
- 877
- Reaction score
- 1,700
View: https://mobile.twitter.com/muxelaero/status/1166259652323160065
Bars is now being offered for the Yak-130.
Bars is now being offered for the Yak-130.
Unsurprizing. If it was Irbis deruvative, then - maybe, and even then it's not an AESA.Since 2019. It's just that there seems to be no taker so far.
But old Bars design?
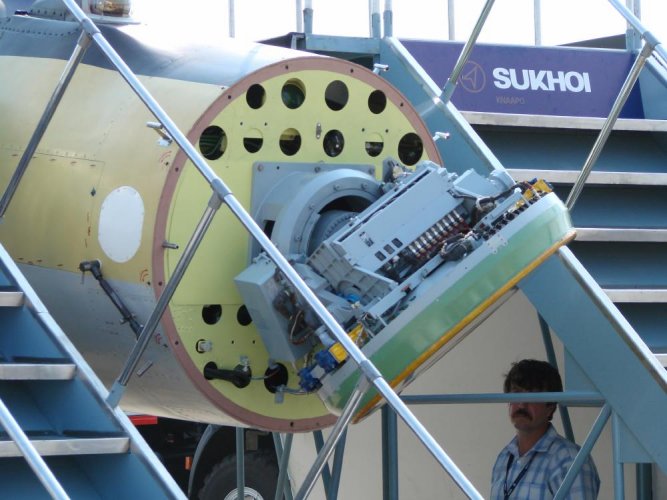
In theory it's possible. Whether it's actually implemented that way is yet another question. It must be noted that the mechanical steering is basically limited to azimuth though.Irbis-e can scan without physically turning the aperture, but the aperture can turn to improve the field of regard. Do you guys think the pilot can steer the aperture a certain way to reduce the RCS of the aircraft?
are you sure about that?, I vaguely remember it can turn in any directionIn theory it's possible. Whether it's actually implemented that way is yet another question. It must be noted that the mechanical steering is basically limited to azimuth though.Irbis-e can scan without physically turning the aperture, but the aperture can turn to improve the field of regard. Do you guys think the pilot can steer the aperture a certain way to reduce the RCS of the aircraft?
I beg to differIt must be noted that the mechanical steering is basically limited to azimuth though.
The Su-35’s air-to-air Phazotron NIIP N-011 multi-mode, look-down/shoot-down radar (which also has an air-to-ground capa- bility out to a range of 124 miles) is sophisti- cated but not up to state-of-the-art Western standards. Typical of Russian radars, it depends more on its enormous power than on sophistication to accomplish search-and- track tasks and overcome countermeasures. Regardless, Sukhoi claims the unit can track up to 15 targets simultaneously while it engages any six at ranges of up to 249 miles. Few Russian aircraft observers truly believe the latter, but military strategists often use it anyway for threat analysis purposes.
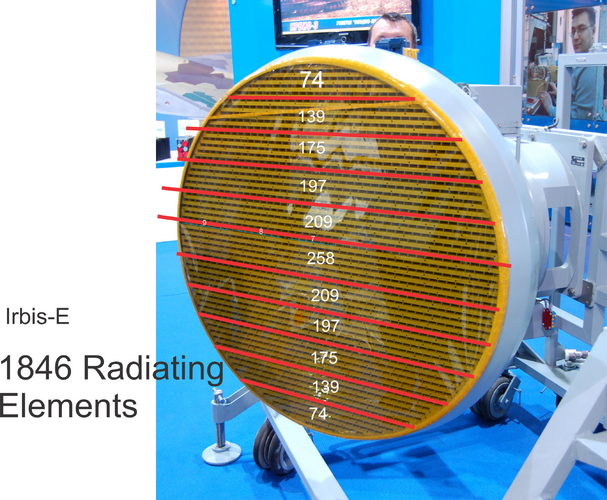
There isa simple answer - mid-life upgrades. I saw a picture from presentation where was timieline of Indian N011M variants. with first variant being purely A2A, with A2G and other improvements coming through with upgradesand new production blocks.The inconsistency is probably caused by use of range of different PD and PFA's. Bars has always been credited with 250-300 km range. It could be however for PD-50%, while the 110 km range figure is for PD-90%.
There isa simple answer - mid-life upgrades. I saw a picture from presentation where was timieline of Indian N011M variants. with first variant being purely A2A, with A2G and other improvements coming through with upgradesand new production blocks.
N001VEP also has 150km range for its long range search. I notice a number of Russian radars have similar range to their equivalent. Like Zhuk-ME and N019M1.That cant explain differences and inconsistencies in range figures tho.. like Initial N011M Bars was always rated for at least 150 km range for a "fighter" sized target then it's credited with 330 km range for Su-27's. That's in some 2005's, now is 2024.
Yeah but not sure if you can compare it with Bars, as it's a much newer more advanced design.N001VEP also has 150km range for its long range search. I notice a number of Russian radars have similar range to their equivalent. Like Zhuk-ME and N019M1.
I’m actually curious, as I understand it some parts of the N001VEP might be better, like the Baguet series 55-04.02 processors were not used on (at least the initial variants) of Bars. Bars seems to have been forced early on to rely on legacy Soviet components, I’m not sure what later upgrades entailed.Yeah but not sure if you can compare it with Bars, as it's a much newer more advanced design.
That 150 km range is probably obtained through very long dwell time, which may not be realistic for combat scenario.
While I'm largely in the same boat, I want to say that one of the key differences between The Irbis-E & traditional PESAs is the addition of more power via the installation of a second traveling wave tube that, along with improved signal processing & everything else, enhances the overall sensitivity of the radar while also doubling the number of simultaneously tracked & prosecuted targets in comparison to older models, which, interestingly, is also the very same approach that was adopted by The Patriot, although the newer radars are/will be AESAs. Why Russia does not do the same with their Pantsirs, Tors, Buks, S-300s, S-350s, & S-400s, etc., makes absolutely no sense to me.I dont understand a lot of the intricate details of radio electronics and deeply admire stealthflanker types who are gifted with mathematical and engineering acumen. That said I think it is much more complicated than "it isnt aesa". From all I can gather the irbis e is one of the most powerful pesa radars ever made with functions built in to keep it very competitive. From what I gather the beam steering and agility and bandwidth and power are near peer to even very modern aesa radars. There are certain key features missing tho like LPI and the flexibility of having myriad transmitters as opposed to only one with a few concurrent channels.
Can someone with much better knowledge speak on this when they have the time? If I am wrong on anything please correct me and rip what incorrect stuff I've said apart. For example am I right about pesa radars not having LPI ability as it only has a single powerful transmitter? I know irbis is unique in that it does have hundreds of recieve channels but this is a huge difference between pesa and aesa right?
Edit: had to add a thought.
well, maybe this helps slightly, old, dead source , but technically enough:While I'm largely in the same boat, I want to say that one of the key differences between The Irbis-E & traditional PESAs is the addition of more power via the installation of a second traveling wave tube that, along with improved signal processing & everything else, enhances the overall sensitivity of the radar while also doubling the number of simultaneously tracked & prosecuted targets in comparison to older models, which, interestingly, is also the very same approach that was adopted by The Patriot, although the newer radars are/will be AESAs. Why Russia does not do the same with their Pantsirs, Tors, Buks, S-300s, S-350s, & S-400s, etc., makes absolutely no sense to me.
Bottom line - The Irbis-E essentially represents a kind of middle ground between standard PESAs & AESAs. I think.
The baseline N011M radar uses a vertically polarised 0.9 metre diameter aperture hybrid phased array, with individual per element receive path low noise amplifiers delivering a noise figure cited at 3 dB, similar to an AESA. The antenna is constructed using phase shifter and receiver 'stick' modules, a similar technology to early US AESAs."
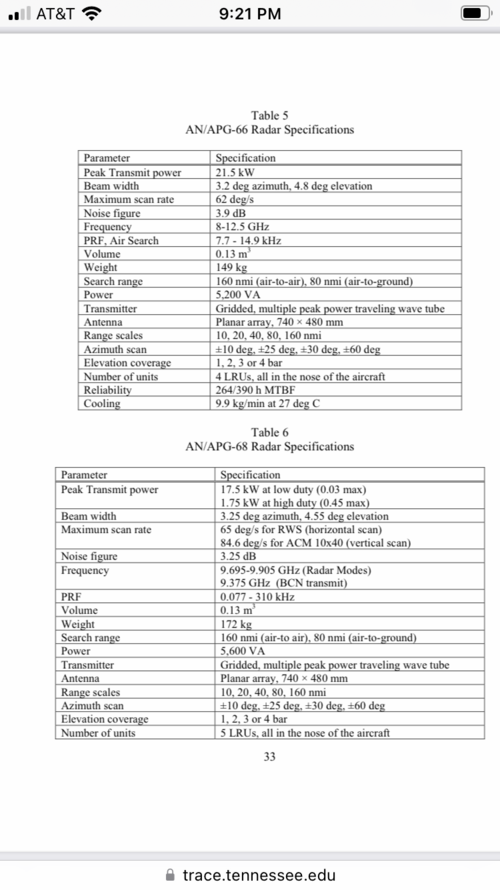
That noise figure is fairly close to apg-68 at 3.25 and less different then the noise gap between apg-68 and 66
Somehow agree.You can't really compare it tho as the LNA for Bars and AESA are in the radiating elements. While APG-66 and 68 is kinda far back. The feed assembly and the path will increase that. It's similar scheme as AN/SPY-1.
The NF Specification is perhaps only the receiver without taking account of the antenna feeds.
It is TWT (like in the above APG-68) or Klystron. Both, are high voltage, vacume tubes.. those works as power amplifiers..And really a neophite question, my understanding is that for modern AESAs the TRMs are either GaA or GaN, with China apparently moving to the next generation GaO TRMs (it matters being an EV and rare earths superpower). But what material is used for the emitter modules of PESAs such as Bars and Irbis, or for older ones like Zaslon, RBE2 etc.?
Somehow agree.
To suplement my post, some link, old known source.. this is second edition..

Introduction To Airborne Radar : GEORGE W. STIMSON : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Introduction to Airborne Radar by G.B.Stimsonarchive.org
Page 477, 478.., 488 ..
And adaptive theshold is on page.. sequentional detection..

Introduction To Airborne Radar : GEORGE W. STIMSON : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Introduction to Airborne Radar by G.B.Stimsonarchive.org
(BTW Such detection, was I think, introduced also in Zaslon.. )
According to APG-68, well, I heard that, in that design was low power amplifier, on back plate of array antena.. similar as in radar of Ammram.. all this is done to put this as close possible to "source".
By the way, nice data. Maybe to be put in F-16 thread..?
It is TWT (like in the above APG-68) or Klystron. Both, are high voltage, vacume tubes.. those works as power amplifiers..
Is there any particular reason as to why an Irbis-E-like upgrade was never applied to The MiG-29? Obviously, there have been improvements in its radars over the years, but none like The Irbis-E, so might that be a result of a space issue in terms of not being able to fit a second twt into, well, such a new radar for The Fulcrum? I'm just curious.well, maybe this helps slightly, old, dead source , but technically enough:
https://www.ausairpower.net/APA-Flanker-Radars.html
There is described "difference" between traditional PESA and "hybrid PESA" used in late Flankers...
From description of BARS radar..:
Thanks for you reply LukaszK, but i meant the material in each individual emitter element such as the 1800 elements in Irbis, not the Chelnok TWT.
According to this link, apparently the material is ferrite, do i understand it correctly, or is in some other material in the contemporary Bars/Irbis radars, since they are described as PESA/AESA hybrids?
Evolution of AESA Radar Technology
Explores the history of AESA radars and how continuing advances in MMIC materials and fabrication technologies, advancing packaging technology and exponential growth in digital circuits opens many possibilities for the futurewww.microwavejournal.com
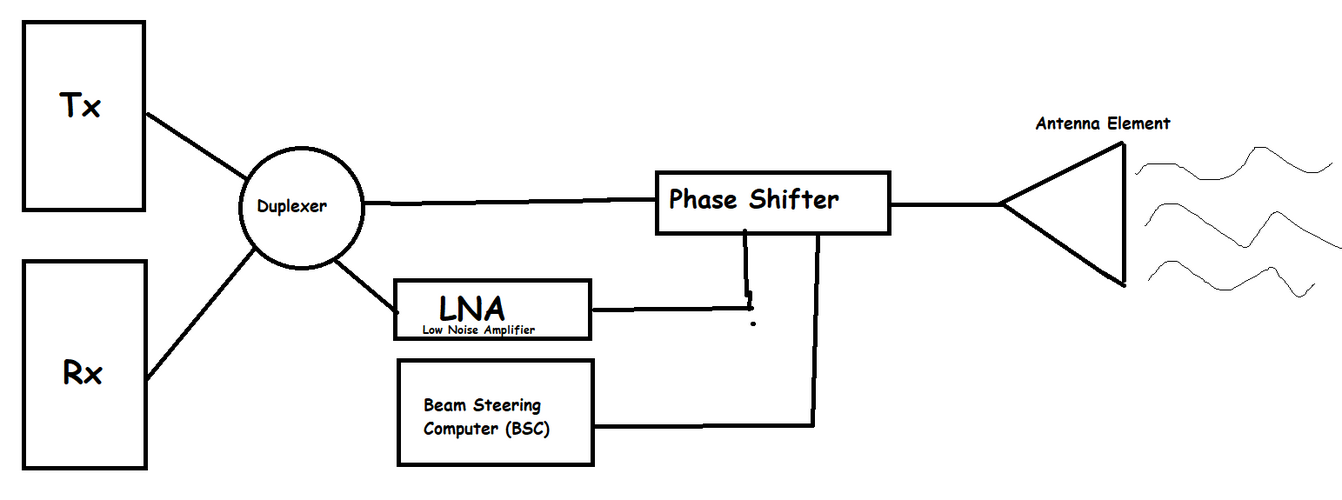


Is there any particular reason as to why an Irbis-E-like upgrade was never applied to The MiG-29?
ThanksTo answer that, you must look deep at Soviet era industries "division" Where each companies have their own "supporting environment".
MiG for example, the radars are built by NIIP Phazotron. Irbis in other hand is developed by NIIP Tikhomirov. Among those companies tehre might be common solution and cooperations (e.g MiG-31 and to some extent Su-27 and MiG-29) But MiG platform are exclusively Phazotron's playgrounds.
Unlike NIIP Tikhomirov however, Phazotron have their own "future" for MiG-29 platform, which as you can see they want AESA. Thus why RP-35 or now you know it as Zhuk-AE was born.
I think the contribution of noise after LNAs is negligible, bcuz it's the entire purpose of LNAs, even the most advanced LNAs degrade SNR, but the reason of this amplification is to ensure that any contribution of downstream noise source is minimized. But the tradeoff is that high gain devices lack linearity which can add disortion to your signals.You can't really compare it tho as the LNA for Bars and AESA are in the radiating elements. While APG-66 and 68 is kinda far back. The feed assembly and the path will increase that. It's similar scheme as AN/SPY-1.
The NF Specification is perhaps only the receiver without taking account of the antenna feeds.
I think the contribution of noise after LNAs is negligible, bcuz it's the entire purpose of LNAs, even the most advanced LNAs degrade SNR, but the reason of this amplification is to ensure that any contribution of downstream noise source is minimized. But the tradeoff is that high gain devices lack linearity which can add disortion to your signals.You can't really compare it tho as the LNA for Bars and AESA are in the radiating elements. While APG-66 and 68 is kinda far back. The feed assembly and the path will increase that. It's similar scheme as AN/SPY-1.
The NF Specification is perhaps only the receiver without taking account of the antenna feeds.
How is Irbis E resistance to jamming?well, maybe this helps slightly, old, dead source , but technically enough:
https://www.ausairpower.net/APA-Flanker-Radars.html
There is described "difference" between traditional PESA and "hybrid PESA" used in late Flankers...
From description of BARS radar..:
"
The BARS is the most advanced radar developed by Russian industry during the 1990s. It is unusual in being designed with a hybrid array arrangement, the receive path using very similar technology to US and EU AESAs, with similar sensitivity and sidelobe performance, but using a Travelling Wave Tube and backplane waveguide feed for the transmit direction, a technology closest to the B-1B and early Rafale EA radars. As such the BARS is a transitional design sitting in between Passive ESAs (PESA) and contemporary AESAs. There is no doubt this design strategy reflected the unavailability to Russian designers of the Gallium Arsenide power transistors used in Western AESAs.
The baseline N011M radar uses a vertically polarised 0.9 metre diameter aperture hybrid phased array, with individual per element receive path low noise amplifiers delivering a noise figure cited at 3 dB, similar to an AESA. The antenna is constructed using phase shifter and receiver 'stick' modules, a similar technology to early US AESAs."
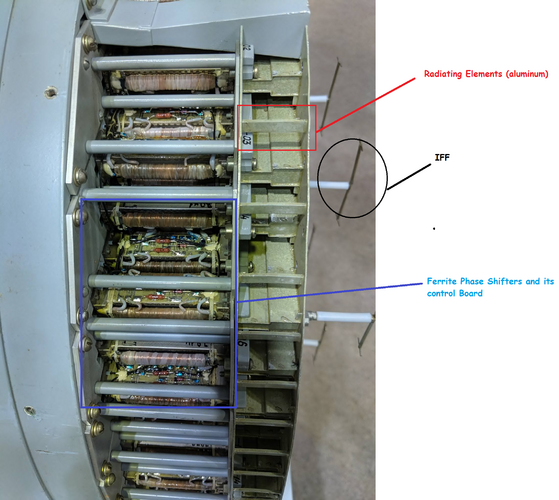
Some comment. Typical, classical PESA was made from single high power generator - like TWT (Klystron). The power was provided by set of waveguides (typically in planes) or optically (generally in ground systems..) to array of passive elements - phase shifters.
Those elements , (like ferrite phase shifters) are controlled electronically and changes phase of each emitted signal.
Signals from all radiating elements forms single beam that is send. Refected from objects... very very weak signal reaches back antenna. The same passive shifters, designed both for handling high power, now are used to shift received signal, with exactly the same phase shift. Next... signals, weak signals, from all array elements are passed and summed to the receiver. Here low power receiver, can finally gain signal and pass to further processing...
This arrangement, has many drawbacks. Array was usually heavy, and has other disadvantages (and advantages).
But from signal and efficiency point of view, this looks like: high power energy is transmitted... first time ,,, some amount of power is lost in wave-guide while on send ... Next ...other power is lost in passive shifters ... On receiving similar happens... very weak signal ... first goes pass by passive snifters, this reduce energy, but worse is that those elements have own noise which is somehow added to very weak signal... then waveguides (once again reduction and noise) and finally this very weak signal reaches to amplifier...
This impact sensitivity. "noise figure" of early PESA was higher than conventional plate arrays (for example +6dB or more comparing to other design).
Lower sensitivity, and losses of power impacts range, that might be lower than in conventional designs, with the same array size and transmitter power.
Of course PESA had other features those, can somehow mitigate above mentioned drawbacks, like:
- possible bigger antenna size in the same airframe - as array could be fixed.
This somehow mitigates decrease of range , as - at least when target is in front of antenna: as effective array area might be higher than in conventional designs...
But for higher angles from array axis, effective array area drops significantly and fast... ( cousins of angle ..). As the array size has tremendous impact on radar performance (gain an beam with) - advantages were rather only for targets in front of plane.
- scanning might be adaptive... with for example dual detection threshold.. usually it was possible to use lower threshold..
In classical design this would lead to high false alarms ratio... as noise ... incidentally might cross threshold.
So in conventional radars, this need to be set high enough to pass only strong signals , and limit false alarms.
But in PESA lower threshold might be used... once signal cross threshold... scanning might immediately stop at that position to check if this is true object or false positive. And it can stay at that position more time than in classical design - to collect more energy. (It can even do monopulse precise coordinate estimation.... if required)
But generally those drawbacks of PESA were very severe. Solution was (analog) AESA in which:
- low power microwave signal is passed from common source via low power wave guides to emitting elements. Here , low power phase shiftier could be applied. Moreover energy of each elements can be precisely and dynamically set. This form "tapering" function - which reduces emitted sidelobes. Finally low power signal to be emitted is amplified in local power transistor . And that is just directly behind emitting elements.. no power is wasted...
- on receive side - is similarly , but in reverse order... very weak signal is directly amplified by receiving, low power, low noise transistor, "just below" the array. NO additional noise is added... this initially gained signal is (either down converted to intermediate frequency, or not) passed via phase shiftier and wave-guides to next stages of receiver.. But as signal is initially gained... noise of other elements has almost no impact on sensitivity.. hence cited above "low noise factors of AESA"
(The next step is digital AESA - where signal to and from elements are passed in digital form... but this is just different story,,,)
Returning to BARS... and IRBIS ... they claimed that this is "hybrid" design. In emitting way - it seems to be very similar to classical PESA.. with all drawbacks... in loosing some energy... lower frequency agility and so on...
But on receiving path .. this looks like more like AESA (at least if we cite the above article). So with low power, low noise transistors just below array and so on. So it might have high sensitivity comparable to AESA. And as author claims... Russian decided on that design, causes they have no technology to produce array of GaAs power transistors. But at reciving part - this is like AESA... even with possibility applying tapering function to reduce sidelobes.
Of course both PESA and AESA design has the same "problem" with high angles targets... parameters of those arrays decreases for high of boresight angles... To mitigate that - cheek arrays are used (like in Su-57) or movable PESA/AESA arrays - like in Su-35 , Grippen or Typhoon...
And comparing Irbit to BARS... BARS was further development of late 80tees design using PESA technology, technology developing that time for N-014
They assembly BARS - developed and made mature design in 90tees. And having this mature design, and experience, after decade, having much more sophisticated components of early 00', just did step further - doing BARS again, but with much more modern elements... This results, as you mentioned , with double transmitter of much more energy, thinner and more nimble antenna, better ..everything...