In the mid-1950s it was decided to increase the Royal Navy presence in the Falkland Islands dependencies. It was hoped to build a new icebreaker and the United States Navy made the plans of the Wind-class icebreaker available. British engines were selected that made the ship much longer. The cost rose and the project was abandoned. HMS Protector, a former net layer, was chosen instead with a minimum of changes. She was reclassified in 1955 as an Antarctic Patrol Ship.
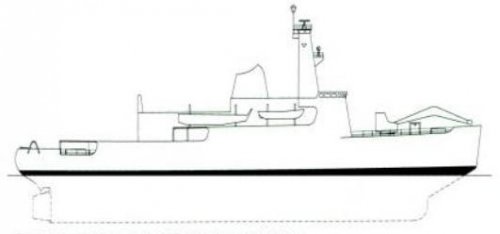
A few years later, another design study was progressed in more detail for a vessel to be called Terra Nova. This impressive icebreaker/oceanographic survey vessel made use of Canadian, American, and Scandinavian experience in its design. Deep displacement was approximately 7,000 tons with dimensions 278 feet by 64 feet. Powerplant suggested was four Ruston AO engines developing 15,000bhp; ASR1 diesels were also considered. The project was canceled in 1967 as an economy measure, her replacement being the Denmark-built Anita Dan. She was converted by Harland & Wolff and renamed HMS Endurance (A 171).
Source: Rebuilding the Royal Navy: Warship Design Since 1945 by DK Brown and George Moore and Wikipedia.
Outboard profile of Design Study I of HMS Terra Nova.
A few years later, another design study was progressed in more detail for a vessel to be called Terra Nova. This impressive icebreaker/oceanographic survey vessel made use of Canadian, American, and Scandinavian experience in its design. Deep displacement was approximately 7,000 tons with dimensions 278 feet by 64 feet. Powerplant suggested was four Ruston AO engines developing 15,000bhp; ASR1 diesels were also considered. The project was canceled in 1967 as an economy measure, her replacement being the Denmark-built Anita Dan. She was converted by Harland & Wolff and renamed HMS Endurance (A 171).
Source: Rebuilding the Royal Navy: Warship Design Since 1945 by DK Brown and George Moore and Wikipedia.
Outboard profile of Design Study I of HMS Terra Nova.