- Joined
- 28 January 2008
- Messages
- 631
- Reaction score
- 480
Some more unearthed notes, this time from 2002.
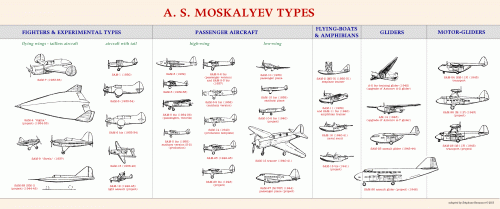
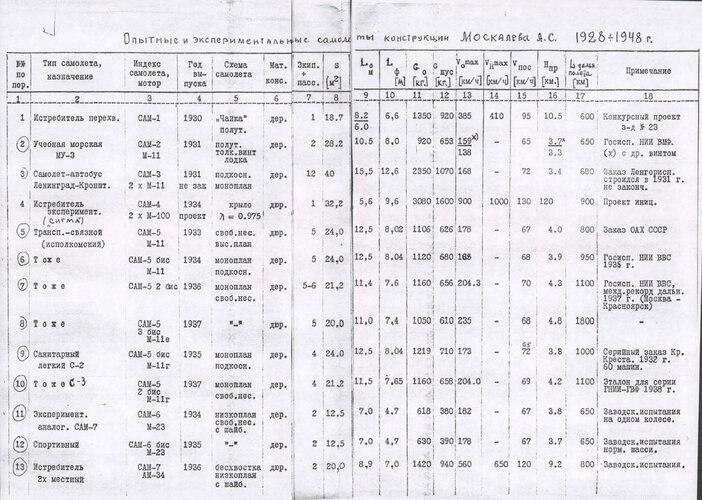
Here is my list of the Soviet designer A.S. Moskalev designations, in manageable size posts, sources at the end of list.
[1930] SAM-1 --- A sesquiplane gull wing monoplane fighter with M-34 engine.
[1930] SAM-2 (MU-3) --- Together with N.G. Mikhelson and O.N. Rozanov, A.S. Moskalev worked on the design for a wooden naval training biplane flying boat powered by an M-11 100 hp pusher engine. It was built at Factory No.23 in Leningrad as a direct development of the earlier Polikarpov (?) MU-3 training aircraft.
[1931] SAM-3 --- Project for twin engine monoplane transport or communications aeroplane. It had an open cockpit, with a high wing.
[1933] SAM-4 Sigma --- A tail less layout with a low aspect ratio wing. It went through several thorough redesigning processes, although always retaining its futuristic wing form.
[1932] SAM-5 --- An all-metal high wing monoplane with a single engine with a maximum speed of 175 km/h and a fixed undercarriage.
[1934] SAM-5bis --- Wooden variant of the SAM-5 with an M-11 engine.
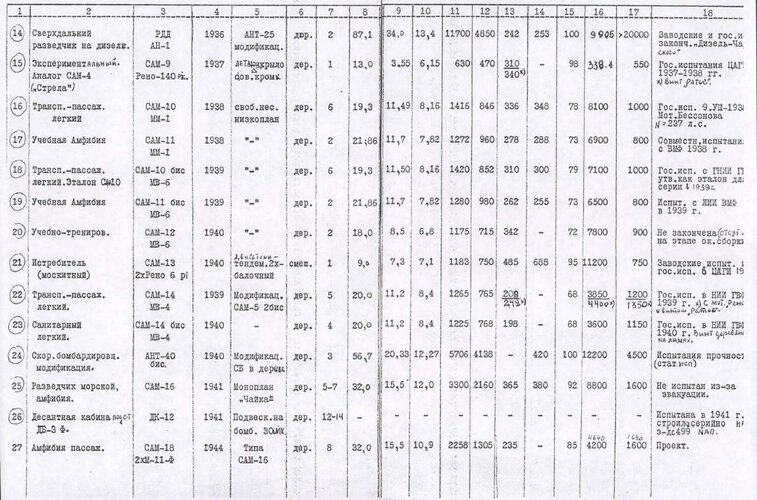
[1936] SAM-5bis S-2 (ambulance) --- Version of the SAM-5bis for the transportation of two litter patients was designated as an S-2 (later this designation passed to the improved ambulance version of Polikarpov U-2).
[1937] SAM-5-2bis --- Conceived with the aim of setting an official international record of flight distance. The aircraft had more advanced design, improved aerodynamics of fuselage, and a cantilever wing of a smaller area. The revised SAM-5-2bis, in a non-record breaking form, remained a small passenger transport capable of carrying 5 people or as an ambulance aircraft.
[1934] SAM-6 --- A dominant wing concept for a single-seat aeroplane with a single-leg undercarriage and rounded end plate fins on wing ends. The fins had no control surfaces and worked at the same time as supporting the equipped skids. Originally the aircraft was built in a two-seat version with a normal empennage. Single engined.
[1934] SAM-6bis --- The SAM-6bis was a two seat version of the SAM-6 research aircraft. It appeared in 1934 with conventional undercarriage and featured spatted wheels and a tandem enclosed cockpit. It was powered by a M-23 engine.
[1934] SAM-7 Sigma --- The SAM-7 had an all-metal construction with smooth skin of varying thickness. The name "Sigma" was reused for this experimental two-seat model. The Moskalev SAM-7 had a layout of a tail less low-wing monoplane with tapered wing and vertical end-plate fins equipped with rudders. There were at least six original Moskalev design bureau diagrams of the SAM-7 design. Each with a different side-fin and rudder configuration.
[1936] SAM-8 --- A development of the Tupolev RDD/ANT-36/ANT-25 with a diesel engine. Work done by Moskalev's factory but designation may not have been official.
[1937] SAM-9 Strela --- The Strela was a single-seat aeroplane with a wing of low aspect ratio, span of only 3.5 m, with a normal vertical fin. The power plant consisted of an inverted air-cooled 140 hp Renault based MV-4 engine. Originally it was to have a Hispano-Suiza engine. Landing gear was three-legged, with a tailskid. First flight on 7 August 1937.
Here is my list of the Soviet designer A.S. Moskalev designations, in manageable size posts, sources at the end of list.
[1930] SAM-1 --- A sesquiplane gull wing monoplane fighter with M-34 engine.
[1930] SAM-2 (MU-3) --- Together with N.G. Mikhelson and O.N. Rozanov, A.S. Moskalev worked on the design for a wooden naval training biplane flying boat powered by an M-11 100 hp pusher engine. It was built at Factory No.23 in Leningrad as a direct development of the earlier Polikarpov (?) MU-3 training aircraft.
[1931] SAM-3 --- Project for twin engine monoplane transport or communications aeroplane. It had an open cockpit, with a high wing.
[1933] SAM-4 Sigma --- A tail less layout with a low aspect ratio wing. It went through several thorough redesigning processes, although always retaining its futuristic wing form.
[1932] SAM-5 --- An all-metal high wing monoplane with a single engine with a maximum speed of 175 km/h and a fixed undercarriage.
[1934] SAM-5bis --- Wooden variant of the SAM-5 with an M-11 engine.
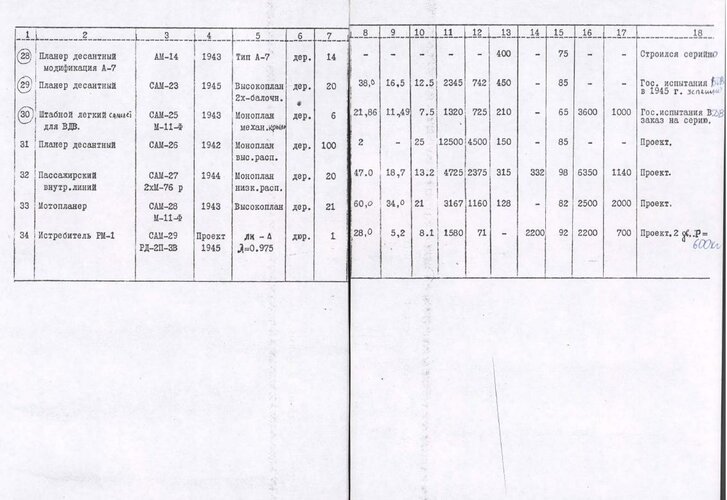
[1936] SAM-5bis S-2 (ambulance) --- Version of the SAM-5bis for the transportation of two litter patients was designated as an S-2 (later this designation passed to the improved ambulance version of Polikarpov U-2).
[1937] SAM-5-2bis --- Conceived with the aim of setting an official international record of flight distance. The aircraft had more advanced design, improved aerodynamics of fuselage, and a cantilever wing of a smaller area. The revised SAM-5-2bis, in a non-record breaking form, remained a small passenger transport capable of carrying 5 people or as an ambulance aircraft.
[1934] SAM-6 --- A dominant wing concept for a single-seat aeroplane with a single-leg undercarriage and rounded end plate fins on wing ends. The fins had no control surfaces and worked at the same time as supporting the equipped skids. Originally the aircraft was built in a two-seat version with a normal empennage. Single engined.
[1934] SAM-6bis --- The SAM-6bis was a two seat version of the SAM-6 research aircraft. It appeared in 1934 with conventional undercarriage and featured spatted wheels and a tandem enclosed cockpit. It was powered by a M-23 engine.
[1934] SAM-7 Sigma --- The SAM-7 had an all-metal construction with smooth skin of varying thickness. The name "Sigma" was reused for this experimental two-seat model. The Moskalev SAM-7 had a layout of a tail less low-wing monoplane with tapered wing and vertical end-plate fins equipped with rudders. There were at least six original Moskalev design bureau diagrams of the SAM-7 design. Each with a different side-fin and rudder configuration.
[1936] SAM-8 --- A development of the Tupolev RDD/ANT-36/ANT-25 with a diesel engine. Work done by Moskalev's factory but designation may not have been official.
[1937] SAM-9 Strela --- The Strela was a single-seat aeroplane with a wing of low aspect ratio, span of only 3.5 m, with a normal vertical fin. The power plant consisted of an inverted air-cooled 140 hp Renault based MV-4 engine. Originally it was to have a Hispano-Suiza engine. Landing gear was three-legged, with a tailskid. First flight on 7 August 1937.