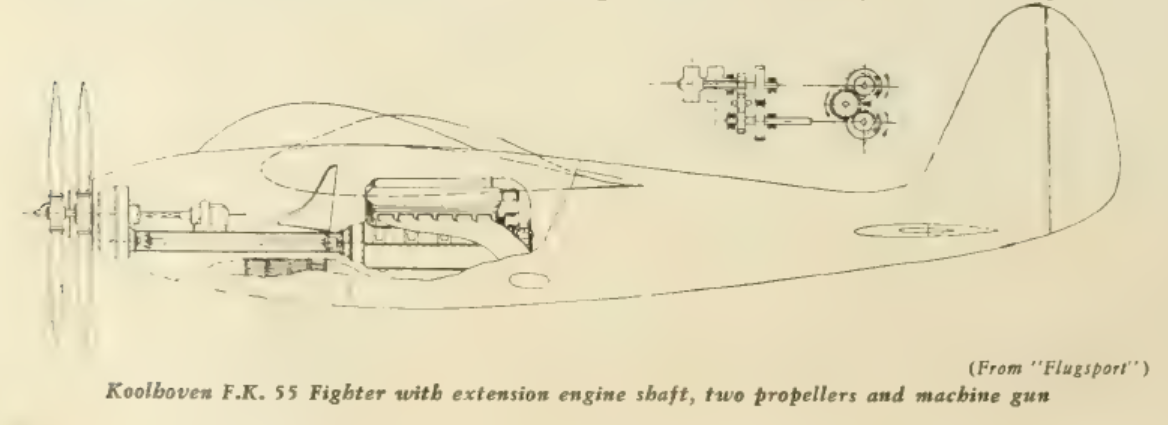
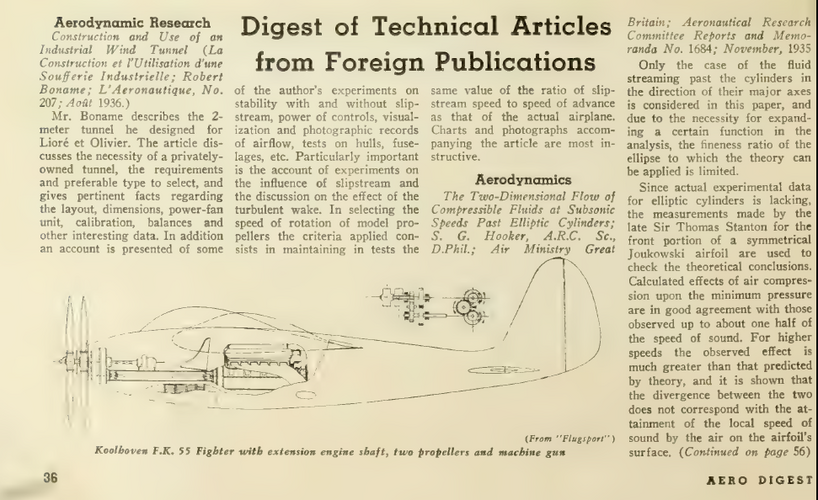
The Lorraine 12Q Eider had an unusually large cylinder capacity for a V-12 engine, namely about 2 825 cubic inches, compared to about 1 865 cubic inches for the Lorraine 12R Sterna, and about 1 755 cu inches for the Lorraine 12H Pétrel...
Just to flesh that out a little ...
Lorraine 12H
Pétrel - 1930 28.73 L (1,753 cid) 60° V-12 engine
- 12H : Bore 145 mm (5.71 in); stroke: 145 mm (5.71 in)
- 12H: Output from 500 hp (12Ha) to 815 hp (12Hgrs)
-- 12H : Direct drive; 675 hp @ 2,200 rpm (normal 500 hp @ 2,250 rpm)
-- 12Ha: Geared; 702 hp @ 2,200 rpm (normal 500 hp @ 2,250 rpm)
-- 12Hars: Geared, supercharged; 720 hp @ 3,000 rpm; 500 hp @ 2,250 rpm
-- 12Hdr: 1931 geared, supercharged; 720 hp @ 2,300 rpm; normal 640 hp
-- 12Hers: 1934 geared, supercharged, higher (6.0:1)
-- 12Hers: Output 720 hp @ 2,650 rpm maintained up to 4,000 m (13,000 ft)
-- 12Hfrs
Normale: 1935 geared, supercharged; output 720 hp @ (??) m
-- 12Hfrs
Chasse : 1935 geared, supercharged; intended for fighter aircraft
-- 12Hfrs
Chasse : 760 hp* @ 2,800 rpm maintained up to 4,000 m (13,000 ft)
-- * Later 12Hfrs had 7.0:1 compression ratios, produced 815 hp @ 2,800 rpm
-- 12Hgrs : 1935 geared, supercharged, 7.0:1 compression; 815 hp @ 2,800 rpm
Lorraine 12Q
Eider - 1930 44.942 L (2,742.5 cid) 60° V-12 engine
- 12Q : Bore 170 mm (6.693 in); stroke 165 mm (6.496 in)
- 12Q : Output 888 hp; application SECM/Amiot Type 141 BCR
Lorraine 12Rcr
Radium - 1931 28.7 L (1,750 cid) 60° IV-12 racing engine
- 12Rcr : Bore 145 mm (5.7 in); stroke 145 mm (5.7 in)
- 12Rcr : Intended output 2,000-2,200 hp; never flown
Lorraine 12Qo
Eider - 1936 46.304 L (2,825 cid) 60° V-12 engine
- 12Qo : Updated and enlarged development of 1930 12Q
Eider
- 12Qo : 'Square'; bore 170 mm (6.693 in); stroke 170 mm (6.693 in)
- 12Qo : 1,000 hp @ 2,350 rpm and 4,000 m (13,000 ft)
Lorraine 12R
Sterna - 1936 30.553 L (1,864.47 cid) 60° V-12 engine
- 12R : Updated, refined, and enlarged
Pétrel (and its replacement)
- 12R : 'Square'; bore 148 mm (5.827 cid); stroke 148 mm (5.827 cid)
- 12R : Output 810 hp @ 2,575 rpm and 4,000 m (13,000 ft)*
-- * Using higher octane fuel, 1,100 hp; 1,350 hp at 3,000 rpm T/O
-- 12R Type 1°: 17:1 gearing; clockwise or anti-clockwise prop rotation
-- 12R Type 2°: 34:21 gearing;
moteur-canon (hollow prop shaft)
-- 12R Type 3°: 2-stage 2-speed supercharger; higher performance**
-- ** 7:1 compression ratio; blower turned at 8.8 x crankshaft speed
-- 12R Type 3°: 900 hp @ 2,700 rpm and 4,000 m (13,000 ft) altitude
-- 12R Type 3°: 1,200 hp for T/O; 850 hp @ 4,500 m (13,800 ft)
-- 12R Type 4°: Direct fuel injection; Szydlowski-Planiol supercharger
-- 12R Type 5°: Remote drive variant w/ contra-props (as per F.K.55)
More details at:
https://enginehistory.org/Piston/Before1925/EarlyEngines/L/Ld.shtml