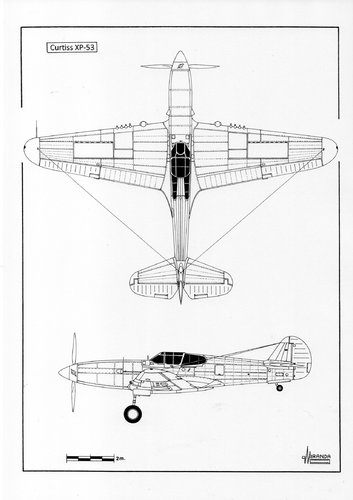
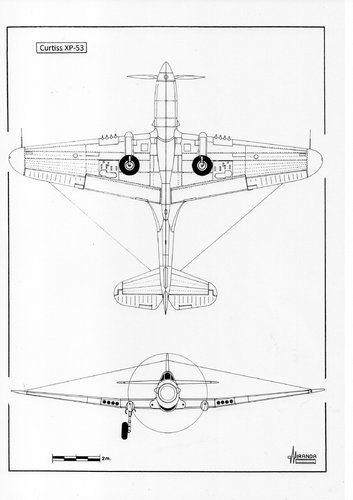
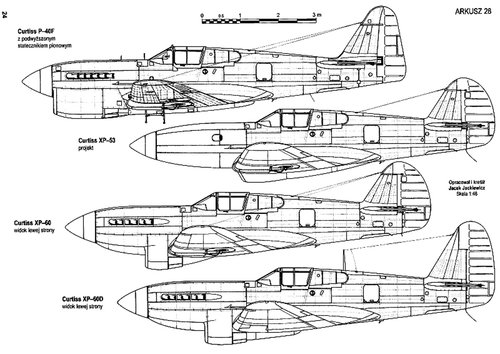
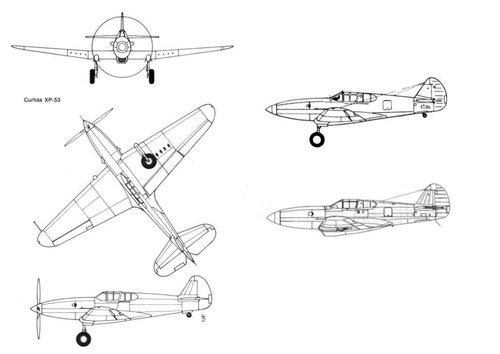
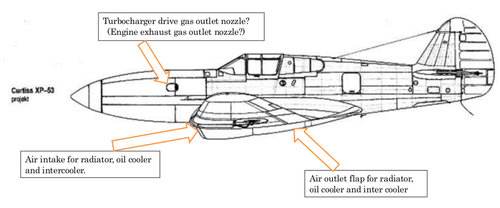
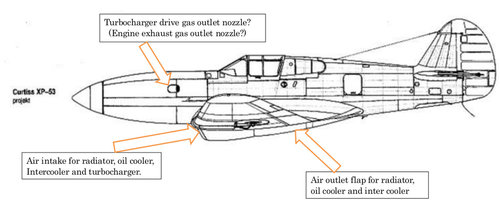
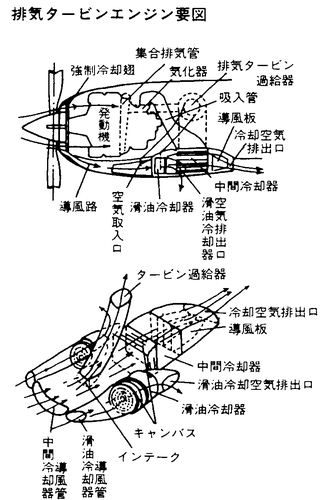
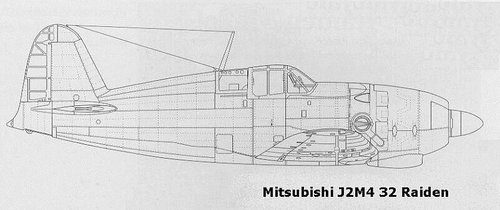
The XP-53 was the second attempt to produce a successor of the P-40, after the cancellation of the ‘european-style fighter’ XP-46.
Curtiss XP-53 technical data
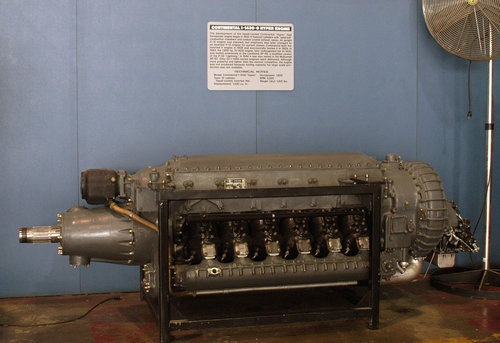
Power plant: one 1,600 hp Continental XIV-1430-3, twelve-cylinder, inverted Vee, liquid cooled engine driving a three-bladed Curtiss-Electric propeller with 11.2 ft of diameter, wingspan: 41.4 ft (12.62 m), length: 35.2 ft (10.74 m), height: 12.3 ft (3.75 m), wing area: 284 sq.ft (25.54 sq.m), estimated maximum speed: 430 mph (692 kph), estimated maximum weight: 10,618 lbs (4,810 kg), estimated service ceiling: 30,500 ft (9,300 m), armament: eight 0.50 cal M2 wing mounted machine guns.
Curtiss XP-53 technical data
Power plant: one 1,600 hp Continental XIV-1430-3, twelve-cylinder, inverted Vee, liquid cooled engine driving a three-bladed Curtiss-Electric propeller with 11.2 ft of diameter, wingspan: 41.4 ft (12.62 m), length: 35.2 ft (10.74 m), height: 12.3 ft (3.75 m), wing area: 284 sq.ft (25.54 sq.m), estimated maximum speed: 430 mph (692 kph), estimated maximum weight: 10,618 lbs (4,810 kg), estimated service ceiling: 30,500 ft (9,300 m), armament: eight 0.50 cal M2 wing mounted machine guns.
Attachments
Last edited: