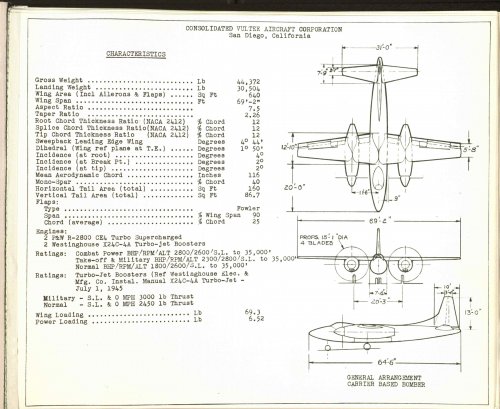
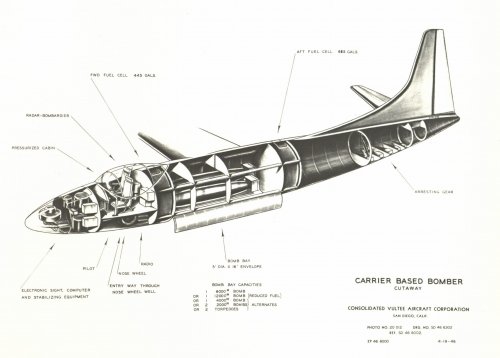
The Navy received three proposals from industry in response to its RFP for a heavy multi-engine carrier-based bomber for Outline Specification 106. The winner was North American, with what became the AJ Savage. Douglas was a close second with its Model 566. Consolidated Vultee (CV) also proposed but its offer was reportedly rejected because it, in the Navy's estimation, would not provide the minimum 300 nautical-mile mission radius.
Unlike the other two proposals with three engines, two piston and one jet, the CV bomber was powered by four engines, two P&W R-2800s and two Westinghouse 24C jet engines, colocated in the engine nacelles. (The upper exhaust was for the piston engine's turbosupercharger.) At the time of the proposal, the crew requirement was apparently only for a pilot and "bomber"; the AJ had a three-man crew: pilot, bombardier, and a third crew station presumably for the individual who was to arm the bomb (it was usually occupied by a crew chief).
Unlike the other two proposals with three engines, two piston and one jet, the CV bomber was powered by four engines, two P&W R-2800s and two Westinghouse 24C jet engines, colocated in the engine nacelles. (The upper exhaust was for the piston engine's turbosupercharger.) At the time of the proposal, the crew requirement was apparently only for a pilot and "bomber"; the AJ had a three-man crew: pilot, bombardier, and a third crew station presumably for the individual who was to arm the bomb (it was usually occupied by a crew chief).