- Joined
- 1 May 2007
- Messages
- 2,531
- Reaction score
- 1,739
this aircraft was mentioned in the thread here :-
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php/topic,5580.msg195805.html#msg195805
But as far as i can tell, we have no thread for the aircraft itself. So...
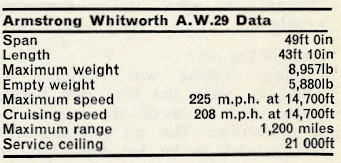
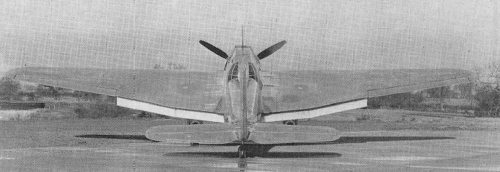
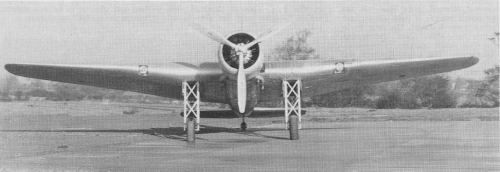
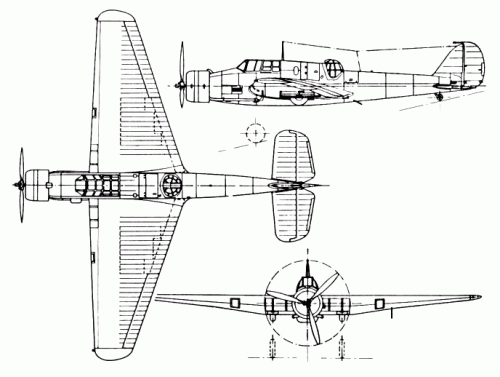
Designed to meet specification P27/32 for a single engined day bomber, the AW.29 was to be Armstrong Whitworth's only single engined monoplane. Proposals were submitted in October 1933, leading to the go-ahead, in June 1934, for a single prototype.
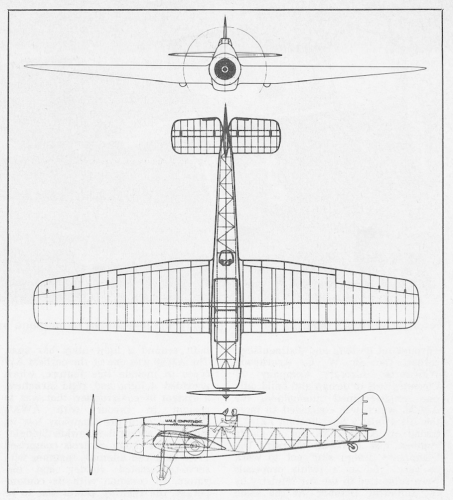
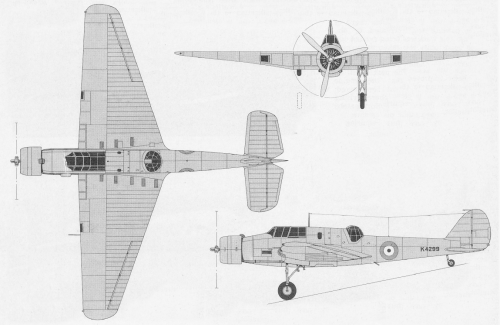
Constructed entirely of metal, the forward fuselage was of light alloy covered steel tubing, while the rear fuselage was a light alloy monocoque, a first for AWA. The wing was also of light alloy construction, the leading edge metal skinned, the remainder covered in fabric, built around a light alloy box spar. The tail surfaces were also of fabric covered metal construction.
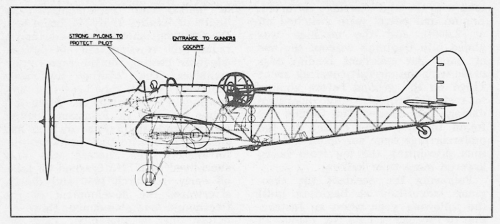
Originally intended to be open, the pilots cockpit was fitted with a sliding canopy, the observer/bomb aimer/wireless operator inhabiting an enclosed turret of AWA design, mounting a single gun. As the two crew members were widely separated, communication was by intercom, or, in an emergency, passing notes along a wire in a tube!
The powerplant was an 870hp Armstrong Siddeley Tiger VIII, driving a DH two-pitch metal propeller.
The bombload, max 1000lbs, was to be carried in compartments in the thick wing. A .303 Vickers gun was also to be mounted on the starboard side of the fuselage, firing forward, but was never fitted.
In 1935, a mailplane variant was proposed, to meet a Canadian requirement. In this version, the pilot's cockpit was moved aft to allow for a large freight compartment. However, nothing further came of this design.
Unfortunately, also in 1935, the competing Fairey design, the Battle-to-be, was ordered off the drawing board. This was probably due to AWA's heavy workload with the Whitley and Ensign aircraft.
However, the prototype was completed, albeit at a low priority, appearing in October 1936. Initially the Air Ministry refused permission for flight testing, stating that the tailwheel provided insufficient ground clearance for the elevator. The tailwheel strut was duly lengthened.
The aircraft's first flight revealed the need for adjustments to the flight controls, and excessively high oil temperatures. While the control issues were soon rectified, the engine problem was not, and, on the second flight, the engine failed in flight. The engine was duly removed and replaced, the air intake being extended over the cowling in the process.
Further flight testing showed no improvement, so the oil cooler was enlarged, and the cowling increased in chord. During these flights, a maximum airspeed of 225kts TAS at 15,100ft was reached.
As there was no prospect of production, It was decided that following completion of Contractor flight trials, the aircraft was to be used for Tiger VIII engine development.
However, during the Contractor's trials, the aircraft suffered a crash-landing following an undercarriage failure. Follwing this, the aircraft remained at the factory until an order was given to repair it and install an Armstrong Siddeley Deerhound engine. During the repairs the turret was removed and the space faired over. The aircraft was then stored, awaiting the installation of a Deerhound engine. It was never installed, the Air Ministry having cancelled the conversion in September 1939, Deerhound development itself being abandoned in early 1940, following the crash of the Whitley Deerhound testbed, K7243.
It was probably realised that a single-engined prototype did not make the best testbed for a new engine type.
Source :- "AW.29; unwanted bomber, 'Aeroplane Monthly', June 1975, pp.299-302.
cheers,
Robin.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php/topic,5580.msg195805.html#msg195805
But as far as i can tell, we have no thread for the aircraft itself. So...
Designed to meet specification P27/32 for a single engined day bomber, the AW.29 was to be Armstrong Whitworth's only single engined monoplane. Proposals were submitted in October 1933, leading to the go-ahead, in June 1934, for a single prototype.
Constructed entirely of metal, the forward fuselage was of light alloy covered steel tubing, while the rear fuselage was a light alloy monocoque, a first for AWA. The wing was also of light alloy construction, the leading edge metal skinned, the remainder covered in fabric, built around a light alloy box spar. The tail surfaces were also of fabric covered metal construction.
Originally intended to be open, the pilots cockpit was fitted with a sliding canopy, the observer/bomb aimer/wireless operator inhabiting an enclosed turret of AWA design, mounting a single gun. As the two crew members were widely separated, communication was by intercom, or, in an emergency, passing notes along a wire in a tube!
The powerplant was an 870hp Armstrong Siddeley Tiger VIII, driving a DH two-pitch metal propeller.
The bombload, max 1000lbs, was to be carried in compartments in the thick wing. A .303 Vickers gun was also to be mounted on the starboard side of the fuselage, firing forward, but was never fitted.
In 1935, a mailplane variant was proposed, to meet a Canadian requirement. In this version, the pilot's cockpit was moved aft to allow for a large freight compartment. However, nothing further came of this design.
Unfortunately, also in 1935, the competing Fairey design, the Battle-to-be, was ordered off the drawing board. This was probably due to AWA's heavy workload with the Whitley and Ensign aircraft.
However, the prototype was completed, albeit at a low priority, appearing in October 1936. Initially the Air Ministry refused permission for flight testing, stating that the tailwheel provided insufficient ground clearance for the elevator. The tailwheel strut was duly lengthened.
The aircraft's first flight revealed the need for adjustments to the flight controls, and excessively high oil temperatures. While the control issues were soon rectified, the engine problem was not, and, on the second flight, the engine failed in flight. The engine was duly removed and replaced, the air intake being extended over the cowling in the process.
Further flight testing showed no improvement, so the oil cooler was enlarged, and the cowling increased in chord. During these flights, a maximum airspeed of 225kts TAS at 15,100ft was reached.
As there was no prospect of production, It was decided that following completion of Contractor flight trials, the aircraft was to be used for Tiger VIII engine development.
However, during the Contractor's trials, the aircraft suffered a crash-landing following an undercarriage failure. Follwing this, the aircraft remained at the factory until an order was given to repair it and install an Armstrong Siddeley Deerhound engine. During the repairs the turret was removed and the space faired over. The aircraft was then stored, awaiting the installation of a Deerhound engine. It was never installed, the Air Ministry having cancelled the conversion in September 1939, Deerhound development itself being abandoned in early 1940, following the crash of the Whitley Deerhound testbed, K7243.
It was probably realised that a single-engined prototype did not make the best testbed for a new engine type.
Source :- "AW.29; unwanted bomber, 'Aeroplane Monthly', June 1975, pp.299-302.
cheers,
Robin.