You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
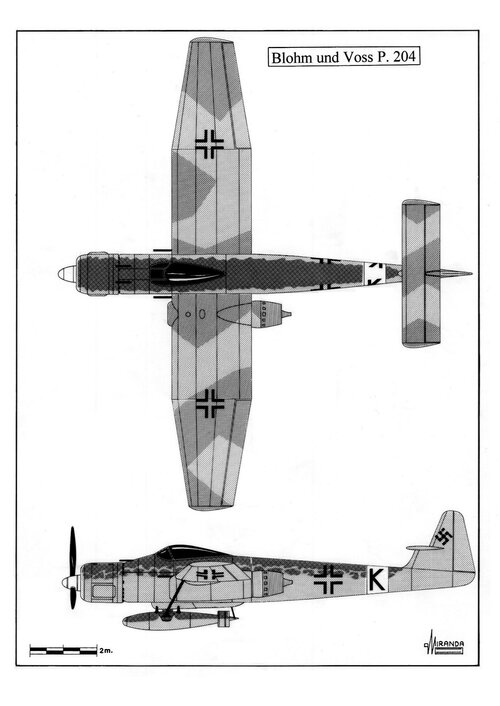
Aircraft intended for carrying the Blohm & Voss BV 246 "Hagelkorn"
- Thread starter kiradog
- Start date
Draaaaag! 
sgeorges4
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 8 October 2017
- Messages
- 665
- Reaction score
- 328
Hello, I know it was testesd on a 190 and that it was apparently considered for a blohm und voss project, where there other planes considered for this glide bomb?
Thanks for your answers, I got the revell 190 with bv 246 in my stash for a what if build and may get more 246 if I get the modellcollect horten XVIII
Thanks for your answers, I got the revell 190 with bv 246 in my stash for a what if build and may get more 246 if I get the modellcollect horten XVIII
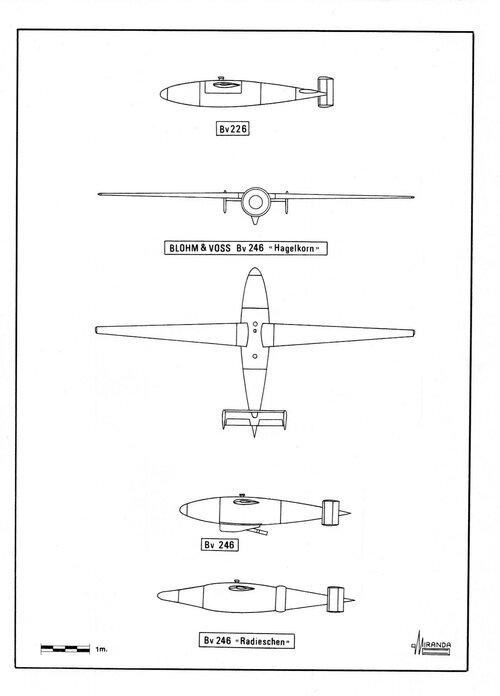
Blohm und Voss BV 226
The Blohm und Voss BV 226 was an unpowered glide bomb with infra-red terminal guidance system.
It was designed in summer 1943 as anti-ship, air-launched, fire-and-forget missile. A Heinkel He 111 H-15 could carry three BV 226s.
It was hoped that the AEG Netzhaut seeker would be able to detect thermal emissions from ships forming Arctic convoys or naval anti-aircraft artillery fire during a combined attack with dive bombers, while keeping the carrier plane out of AA fire range.
The project was cancelled on December 12, 1943 when all technical resources were employed in the creation of Spanner-Anlage infra-red seekers for the Dornier Do 17 Z-10 night fighters.
BV 226 technical data
Wingspan: 6.4 m, length: 3.5 m, height: 0.66 m, fuselage diameter: 0.58 m, wing area: 1.47 sq. m.
In 1944 Blohm und Voss decided to continue developing the weapon, as the BV 246 Hagelkorn, using different types of guidance systems.
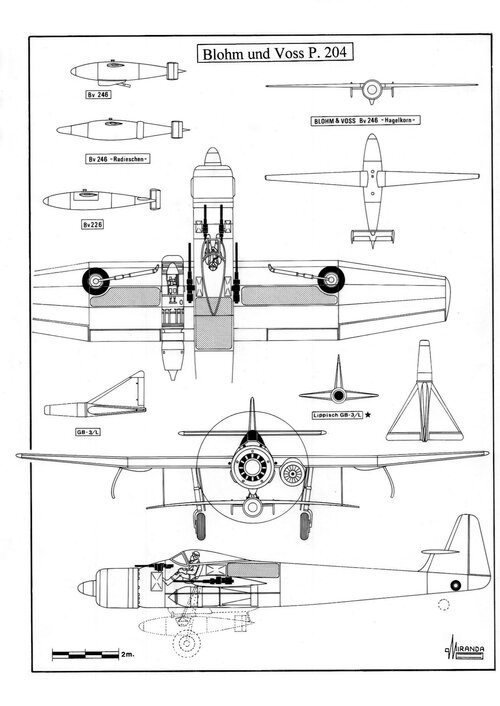
Project 246 was proposed to OKL as an easy-to-manufacture air-to-air or air-to-ground missile using non-strategic materials in competition with Henschel Hs 293D and Lippisch GB 3/L glide bombs.
The fuselage would be constructed with welded sections of 16 gauge mild steel (Stahl 535), the tail surfaces with wood/plywood Lignidur and the wings with die-cast concrete Magnesit-Zement.
Directional information was provided by the IR seeker and the only control surfaces were on the tail surfaces. One Askania gyro-control unit stabilized the bomb in all three axes.
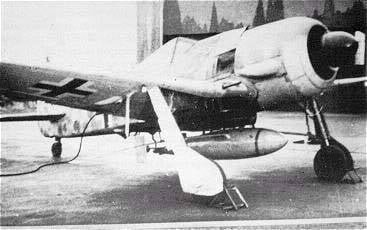
Hagelkorn had a clean, cigar shaped fuselage and a shoulder mounted wing with 25:1 glide ratio which permitted a range of 175 km when it was dropped from 7,000 meters altitude.
BV 246 was proposed in thirteen variants:
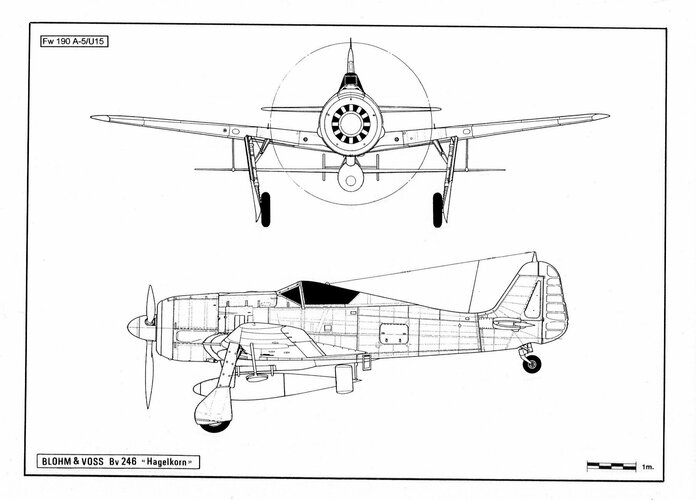
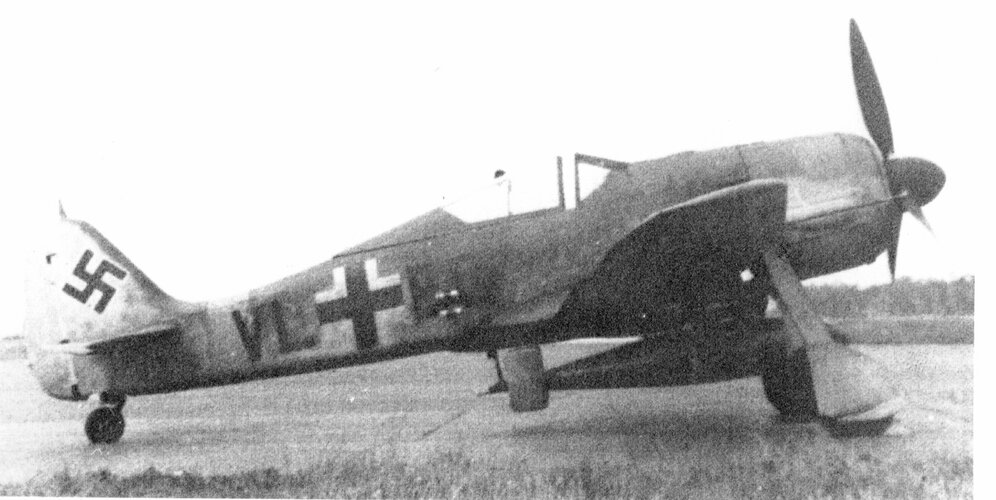
-BV 246 A-1, anti-ship glide bomb to be radio-guided to its target from a parent carrier aircraft (Fw 190 A-6, Fw 190 G-8, He 111 H-15, Ju 88 A-4 or Ju 188 A).
Technical data
Wingspan: 6.4 m, length: 3.39 m, height: 0.65 m, fuselage diameter: 0.58 m, wing area: 1.47 sq. m, Max weight: 700 kg, Max speed: 450 km/h, range: 175 Km when it was dropped from 7,000 meters altitude, warhead: 450 kg of Amatol 39 A H.E. with Z66 impact fuse.
-BV 246 B-1, anti-ship, radio-guided glide bomb with 30:1 glide ratio and 210 km range.
Technical data
Wingspan: 6.4 m, length: 3.53 m, height: 0.65 m, fuselage diameter: 0.54 m, wing area: 1.47 sq. m, Max weight: 730 kg, Max speed: 450 km/h, range: 175 Km when it was dropped from 7,000 meters altitude, warhead: 435 kg of Amatol 39 A H.E. with Z80 impact fuse.
-BV 246 B-2, long range glide bomb with ZSG Radieschen ultra-short wave passive homing device. It was intended for use against Allied Loran navigational radio stations based in the south of England.
Technical data
Wingspan: 6.4 m, length: 4.03 m, height: 0.65 m, fuselage diameter: 0.54 m, wing area: 1.47 sq. m, Max weight: 730 kg, Max speed: 450 km/h, range: 175 Km when it was dropped from 7,000 meters altitude, warhead: 435 kg of Amatol 39 A H.E. with Z80 impact fuse.
-BV 246 E-1, test bench from the Kehl/Strassburg guidance system developed for the AA missile Wasserfall and the Düsseldorf/Detmold guidance system for the airborne AA missile X4.
-BV 246 E-2, towed fuel tank for the Messerschmitt Me 262 jet fighter.
-BV 246 E-3, version of the E-1 fitted with smoke generator and Eberspächer whistles.
-BV 246 F-1, radio-controlled target for Flak training, with 5 m. wingspan, 4.2 m. length, 1:7 glide ratio and 49 km range launches from 7,000 m.
-BV 246 F-2, B-2 airframe with unknown guidance system.
-BV 246 F-3, B-2 airframe with infra-red guidance system.
-BV 246 F-4, B-2 airframe with Blaupunkt Tonne television guidance system.
-BV 246 F-5, B-2 airframe with FM jam-proof radio-control.
-BV 246 F-6, high-altitude launched glide bomb with unknown guidance system.
-BV 246 P-1, B-2 airframe with Telefunken Knickbein guidance system.
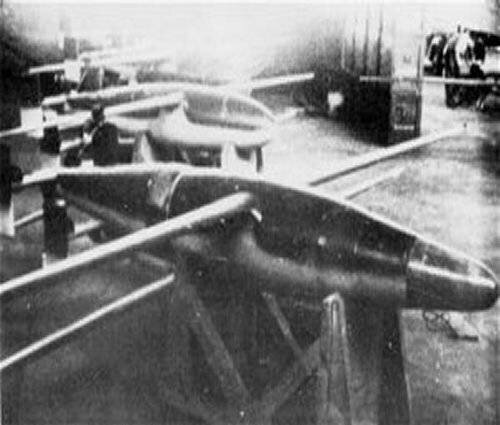
Between December 12,1943 and February 26, 1944 the Henschel Company built 1,100 Hagelkorn units of all types except the B-1 series which was manufactured by Blohm und Voss.
In August 1944, 218 prototypes of the B, E and F series were tested in Karslhagen by the KG 101.
At the end of 1944, at Unterlüss Proving Ground, launch tests were carried out at different speeds using 238 B-series prototypes and the Fw 190 A-5/U15 (VL + FG).
These tests were not successful since the gyroscopic stabilization system failed frequently.
The project was cancelled in March 1944 because a reliable jam-proof guidance system could not be developed.
Attachments
sgeorges4
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 8 October 2017
- Messages
- 665
- Reaction score
- 328
I didn't knew other variants of the 190 could carry it too, revell give a A8 basis:
Similar threads
-
-
-
Blohm und Voss P.173.02 - Long range bomber project
- Started by kiradog
- Replies: 13
-
Blohm & Voss BV 246 Hagelkorn for anti-shipping guidance system questions
- Started by Stuka_Hunter
- Replies: 11
-
Secret Projects of the Luftwaffe: Blohm & Voss BV 155 by Dan Sharp
- Started by newsdeskdan
- Replies: 65